Auditing - Duties of an Auditor [Sec.143] | 12th Auditing : Chapter 9 : Qualifications, Rights and Duties of Auditor
Chapter: 12th Auditing : Chapter 9 : Qualifications, Rights and Duties of Auditor
Duties of an Auditor [Sec.143]
Duties of an Auditor [Sec.143]
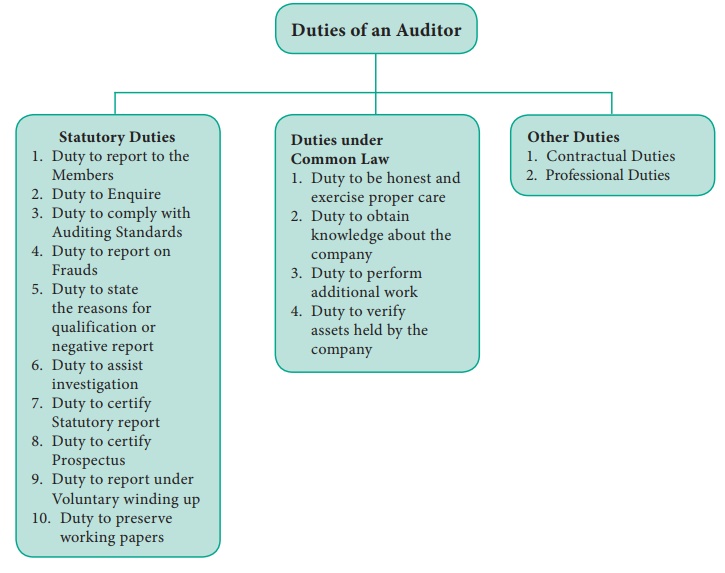
1. Statutory Duties
1. Duty to report to the Members [Sec.143 (3)]:
The
auditor shall make a report to the members of the company on accounts and
financial statements examined by him.
The
report shall state:
a. Whether
he has sought and obtained all necessary information and explanations.
b. Whether
proper books of accounts has been kept.
c.
Whether company’s Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss account are in agreement
with books of accounts and returns.
2. Duty to Enquire [Sec.143 (1)]:
It is
the duty to inquire into the following matters:
·
Whether loans and advances made by the company
based on security have been properly secured and whether the terms on which
they have been made are prejudicial to the interests of the company or its
members.
·
Whether transactions of the company, which are
represented merely by book entries, are prejudicial to the interests of the
company.
·
Whether loans and advances made by the company
have been shown as deposits.
·
Whether personal expenses have been charged to
revenue account.
·
Whether it is stated in the books and documents
of the company that any shares have been allotted for cash, whether cash has
actually been received in respect of such allotment, and if no cash has
actually been so received, whether the position as stated in the account books
and the balance sheet is correct, regular and not misleading.
3. Duty to comply with Auditing Standards [Sec.143 (9)]:
·
Every auditor shall comply with the auditing
standards.
·
The Central Government shall notify standards
in consultation with National Financial Reporting Authority, (NFRA).
·
The government
shall also notify that auditor’s report shall include a
statement on such matters as notified.
4. Duty to report on Frauds [Sec. 143 (12)]:
When an
auditor suspects an offence involving fraud is being committed by officers or
employees of the company, he shall immediately report the matter to the Central
Government in such manner as may be prescribed.
5. Duty to state the reasons for qualified
or negative report [Sec.143 (4)]:
In case
of negative or qualified report, the reasons must be stated in the report.
6. Duty to assist investigation:
It is
the important duty of the auditor to assist the investigator to investigate the
affairs of the company. Further, it is the duty of the auditor,
·
To provide and preserve the necessary documents
which are in his custody to the investigator, and
·
To assist the investigator by providing all
assistance in connection with the investigation.
7. Duty to certify Statutory Report: The
auditor has to certify statutory report as correct to the extent of –
·
Shares allotted by the company,
·
Cash received in respect of such shares, and
·
An abstract of receipts and payments of the
company.
8. Duty to certify Prospectus:
It is
the duty of auditor to certify a report showing statement of profits or losses
and assets and liabilities of the company and its subsidiaries. The report
shall also include rates of dividend paid by the company for each of five
financial years preceding the issue of prospectus.
9. Duty to report under Voluntary winding up:
When the
company proposes for voluntary winding up, directors of the company have to
make a declaration of solvency. The auditor has to certify a report upon the
solvency based on the Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet.
10. Duty to preserve Working Papers: It is
the duty of an auditor to preserve and produce all books and papers relating to
the company which are in his custody and to assist the inspector appointed by
the government for investigation.
2. Duties under Common Law
1. Duty to be honest and exercise proper care:
The auditor
should be straightforward, honest and tactful and must not be influenced by
others in discharge of his duties. He should be careful and cautious in
performing his duties.
2. Duty to obtain knowledge about the company:
He
should obtain detailed knowledge about the activities and affairs of the
company.
3. Duty to perform additional work: The
auditor besides performing the statutory duties is bound to perform additional
work by passing a resolution in the general meeting or making a provision in
the Articles of Association of the company.
4. Duty to verify assets held by the company:
It is
the duty of the auditor to verify assets of the company.
3. Other Duties
1. Contractual Duties:
The
auditor’s duty will depend upon the terms and conditions of his appointment
between him and the party who appointed him.
1. Professional Duties:
The
auditor has to observe the ethics given by the Institute of Chartered
Accountants of India. He should correspond with the previous auditor before
accepting the assignment.
Related Topics