Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Antimycobacterial Drugs
Drugs Used In Tuberculosis
DRUGS USED IN TUBERCULOSIS
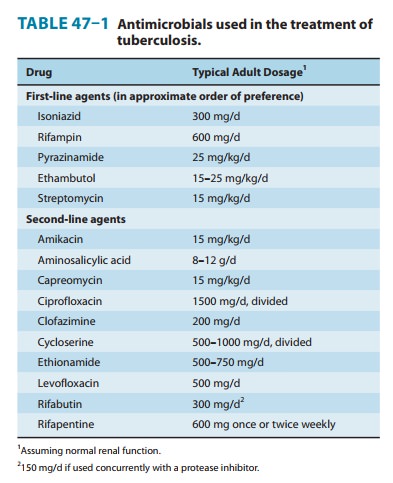
Isoniazid (INH), rifampin (or other rifamycin), pyrazinamide,
ethambutol, and streptomycin are the five first-line
agents fortreatment of tuberculosis (Table 47–1). Isoniazid and rifampin are
the most active drugs. An isoniazid-rifampin combination admin-istered for 9
months will cure 95–98% of cases of tuberculosis caused by susceptible strains.
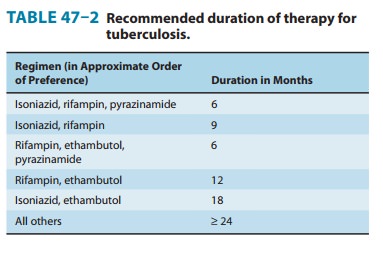
The addition of pyrazinamide to an isoniazid-rifampin combination for the first
2 months allows the total duration of therapy to be reduced to 6 months without
loss of efficacy (Table 47–2). In practice, therapy is initiated with a
four-drug regimen of isoniazid, rifampin, and pyrazinamide plus either
ethambutol or streptomycin until susceptibility of the clinical isolate has
been determined. Neither ethambutol nor streptomycin adds substantially to the
overall activity of the regimen (ie, the duration of treatment cannot be
further reduced if either drug is used), but they provide additional coverage
if the isolate proves to be resistant to isoniazid, rifampin, or both. The
prevalence of isoniazid resistance among clinical isolates in the United States
is approximately 10%. Prevalence of resistance to both isoniazid and rifampin
(ie, multidrug resistance) is about 3%.
Related Topics