Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 5 : Digestion and Absorption
Digestive glands
Digestive
glands
Digestive
glands are exocrine glands which secrete biological catalysts called enzymes.
The digestive glands associated with the alimentary canal are salivary glands,
liver and pancreas. Stomach wall has gastric glands that secrete gastric juice
and the intestinal mucosa secretes intestinal juice.
Salivary glands
There are
three pairs of salivary glands in the mouth. They are the largest parotids
gland in the cheeks, the sub-maxillary/ sub-mandibular in the lower jaw and the
sublingual beneath the tongue. These glands have ducts such as Stenson’s duct,
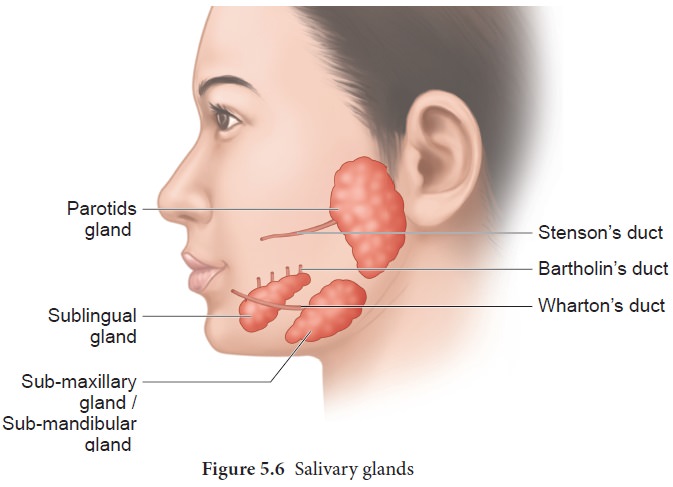
Wharton’s duct and Bartholin’s duct or duct of
Rivinis respectively (Figure. 5.6). The
salivary juice secreated by the salivary glands reaches the mouth through these
ducts. The daily secretion of saliva from salivary glands ranges from 1000 to
1500mL
Gastric glands
The wall of the stomach is lined by gastric glands. Chief cells or peptic cells or zymogen cells in the gastric glands secrete gastric enzymes and Goblet cells secrete mucus. The Parietal or oxyntic cells secrete HCl and an intrinsic factor responsible for the absorption of Vitamin B12 called Castle’s intrinsic factor.
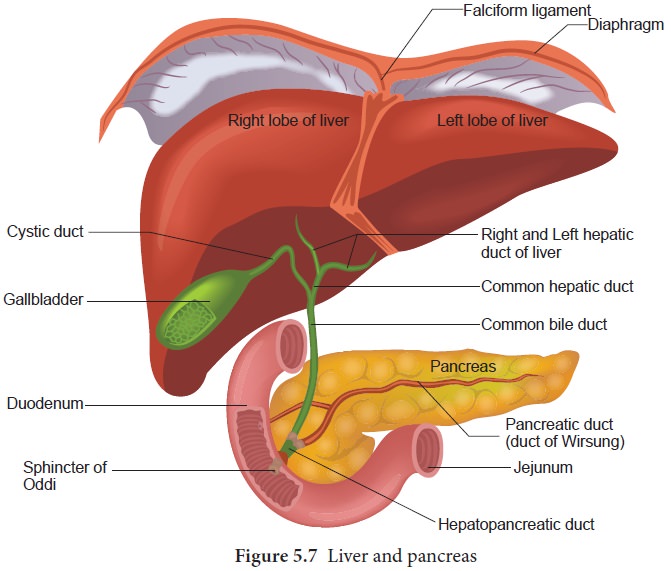
Liver
The
liver, the largest gland in our body is situated in the upper right side of the
abdominal cavity, just below the diaphragm. The liver consists of two major
left and right lobes; and two minor lobes. These lobes are connected with
diaphragm. Each lobe has many hepatic lobules (functional unit of liver) and is
covered by a thin connective tissue sheath called the Glisson’s capsule. Liver cells (hepatic cells) secrete
bile which is stored and concentrated in a thin muscular sac called the gall
bladder. The duct of gall bladder (cystic duct) along with the hepatic duct
from the liver forms the common bile duct. The bile duct passes downwards and
joins with the main pancreatic duct to form a common duct called
hepato-pancreatic duct. The opening of the hepato-pancreatic duct into the
duodenum is guarded by a sphincter called the sphincter of Oddi (Figure.5.7).
Liver has high power of regeneration and liver cells are replaced by new ones
every 3-4 weeks.
Apart
from bile secretion, the liver also performs several functions
1. Destroys
aging and defective blood cells
2. Stores
glucose in the form of glycogen or disperses glucose into the blood stream with
the help of pancreatic hormones
3. Stores
fat soluble vitamins and iron
4. Detoxifies
toxic substances.
5. Involves in the synthesis of non-essential amino acids and urea.
Pancreas
The
second largest gland in the digestive system is the Pancreas, which is a yellow
coloured, compound elongated organ consisting of exocrine and endocrine cells.
It is situated between the limbs of the ‘U’ shaped duodenum. The exocrine
portion secretes pancreatic juice containing enzymes such as pancreatic amylase,
trypsin and pancreatic lipase and the endocrine part called Islets of
Langerhans secretes hormones such as insulin and glucagon. The pancreatic duct
directly opens into the duodenum.
Related Topics