Chapter: 11th Chemistry : UNIT 12 : Basic concepts of organic reactions
Different types of organic reactions
Different
types of organic reactions
Organic
compounds undergo many number of reactions, however in actual sense we can fit
all those reactions into the below mentioned six categories.
• Substitution reactions
• Addition reactions
• Elimination reactions
• Oxidation and reduction reactions
• Rearrangement reactions
• Combination of the above
1. Substitution reaction (Displacement reaction)
In
this reaction an atom or a group of atoms attached to a carbon atom is replaced
by a new atom or a group of atoms. Based on the nature of the attacking
reagent, this reactions can be classified as
i.
Nucleophilic substitution
ii.
Electophilic substitution
iii.
Free radical substitution
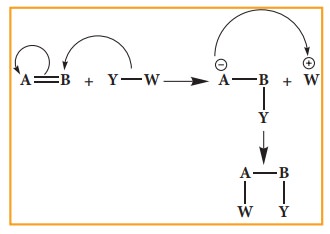
i. Nucelophilic substituion:
This
reaction can be represented as
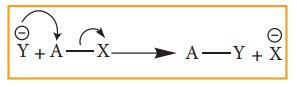
Here
Y– is the incoming nucleophile or and attacking species and x– is the leaving
group.
![]()
![]() Example: Hydrolysis of alkyl halides
Example: Hydrolysis of alkyl halides
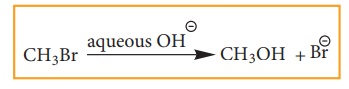
Aliphatic nucleophilic substitution
reactions take places either by SN1 or SN2 mechanism.
Detailed study of the mechanisms is given in unit 14.
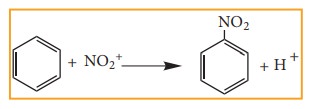
ii. Electrophilic Substitution
Example: Nitration of Benzene
Mechanism of aromatic electrophilic
substitution reactions (EAS) is discussed in detail in unit 13.
iii. Free radical substitution
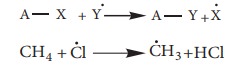
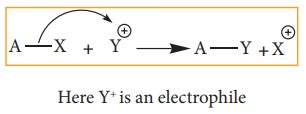
Aliphatic
electrophilic substitution
A
general aliphatic electrophilic substitution is represented as
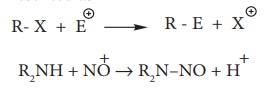
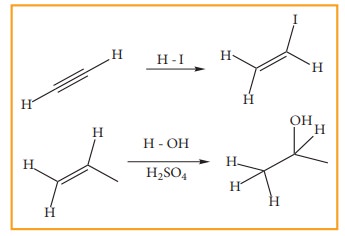
2. Addition reactions
It
is a characteristic reaction of an unsaturated compound (compounds containing
C-C localised double or triple bond). In this reaction two molecules combine to
give a single product. Like substitution this reaction also can be classified
as nucleophilic, electrophilic and freeradical addition reactions depending the
type of reagent which initiates the reaction. During the addition reaction the
hydridisation of the substrate changes (from sp2 → sp3 in the addition reaction of alkenes or sp → sp2 in the addition reaction of alkynes) as only
one bond breaks and two new bonds are formed.
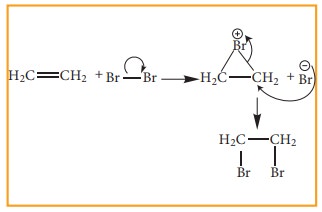
Electrophilic Addition reaction
A
general electrophilic addition reaction can be represented as below.
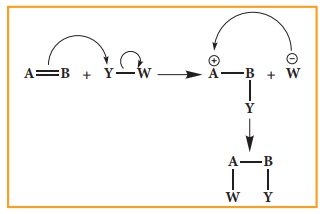
Brominatin
of alkene to give bromo alkane is an example for this reaction.
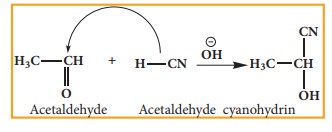
Nucleophilic addition reaction
Example: addition of HCN to acetaldehyde
Free radical addition Reaction:
A
General freeradical addition reaction can be represented as below.
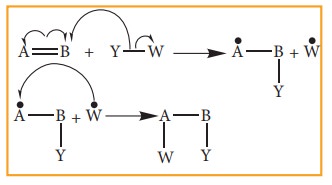
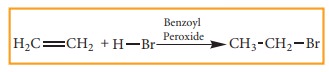
In
the above reaction, Benzoyl peroxide acts as a radical initiator. The mechanism
involves free radicals.
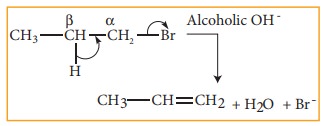
3. Elimination reactions:
In
this reaction two substituents are eliminated from the molecule, and a new C-C
double bond is formed between the carbon atoms to which the eliminated
atoms/groups are previously attached. Elimination reaction is always
accompanied with change in hybridisation.
Example:
n-Propyl bromide on reaction with alcoholic KOH gives propene. In
this reaction hydrogen and Br are eliminated.
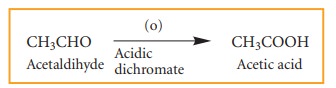
4. Oxidation and reduction reactions:
Many
oxidation and reduction reactions of organic compounds fall into one of the
four types of reaction that we already discussed but others do not. Most of the
oxidation reaction of organic compounds involves gain of oxygen or loss of
hydrogen Reduction involves gain of hydrogen and loss of oxygen.
Examples:
Related Topics