Chapter: Biology of Disease: Membrane, Organelle and Cytoskeletal Disorders
Diagnosis and Treatment of Mitochondrial Disorders
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF MITOCHONDRIAL DISORDERS
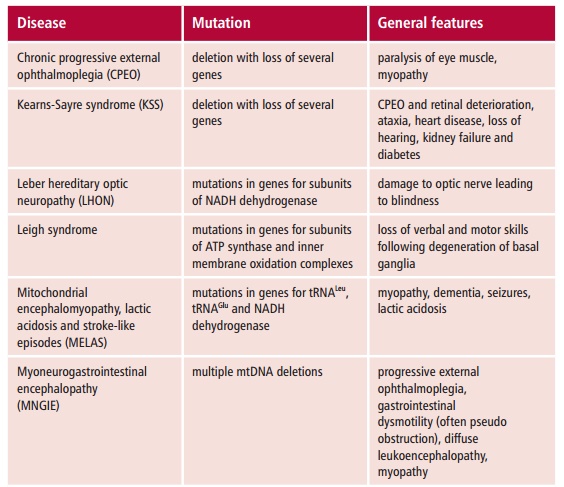
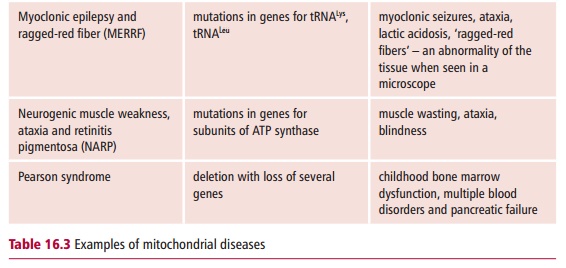
Considerable advances have been made in our understanding of the pathol-ogy of mitochondrial disorders. However, the diagnosis and detection of mtDNA mutations is problematic because of the varied etiology and clinical features of these diseases (Table 16.3). Similarly, predictors of disease progres-sion are also highly unsatisfactory. The concentrations of lactate in plasma, cerebrospinal fluid and urine may, individually or collectively, be increased relative to normal, although these changes are also seen in numerous other clinical conditions. However, a plasma lactate : pyruvate ratio of greater than 40 is usually considered a significant indicator of mitochondrial dysfunc-tion in adults. Other indicators may be the presence of organic acids and myoglobin in the urine, ketoacidosis , and impaired renal, liver and glandular functions.
It would appear that several different approaches to treating and managing mitochondrial disorders will be necessary. Most current treatments of mitochondrial disorders are unsatisfactory and concentrate merely on relieving symptoms. For example, administration of hydrogen carbonate and dialysis may be used to relieve lactate acidosis. Exercise may decrease the proportion of mutant mtDNA in muscle. Treatment with standard vitamins and ubiquinone supplements has been tried but any benefits have yet to be established.
Gene therapy using allotopic expression may offer a permanent cure in the future. The strategy behind this technique is to insert a mitochondrial gene into the nucleus where it is transcribed. The resulting messenger RNA is trans-lated in the cytosol and the protein product is then imported into the mito-chondria where it alleviates the effects of the mtDNA mutation.
Families affected by mitochondrial disorders should be offered counseling on prognosis, risk of recurrence and prevention but even this is complex, because the degree of mutant mtDNA can change dramatically during each transmission of mitochondria from a mother to a child. The advice to affected families on potential reproductive options may therefore be unsatisfactory. Consequently, the clinical management of patients with mitochondrial disorders is largely supportive.
Related Topics