Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : General Anesthetics
Dexmedetomidine - Intravenous Anesthetics
DEXMEDETOMIDINE
Dexmedetomidine
is a highly selective α2-adrenergic agonist. Recognition of the
usefulness of α2 agonists is based on observa-tions of decreased anesthetic
requirements in patients receiving chronic clonidine therapy. The effects of
dexmedetomidine can be antagonized with α2-antagonist drugs. Dexmedetomidine is the
active S-enantiomer of medetomidine,
a highly selective α2-adrenergic agonist imidazole derivative that is used in
veterinary medicine. Dexmedetomidine is water soluble and available as a
parenteral formulation.
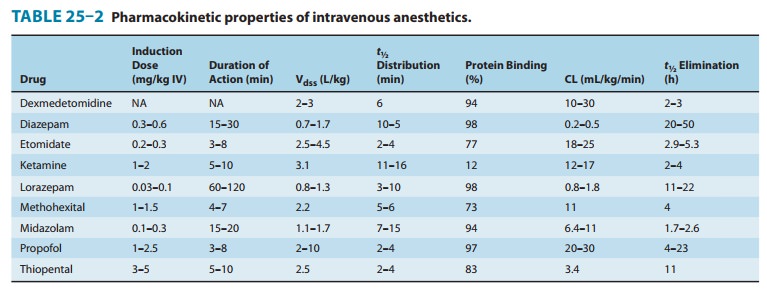
Pharmacokinetics
Dexmedetomidine
undergoes rapid hepatic metabolism involving conjugation, N-methylation, and hydroxylation, followed by con-jugation.
Metabolites are excreted in the urine and bile. Clearance is high, and the
elimination half-time is short (Table 25–2). However, there is a significant
increase in the context-sensitive half-time from 4 minutes after a 10-minute
infusion to 250 minutes after an 8-hour infusion.
Organ System Effects
A. CNS Effects
Dexmedetomidine
produces its selective α2-agonist effects through activation of CNS α2 receptors. Hypnosis
presumably results from stimulation of α2 receptors in the locus caeruleus, and the
analge-sic effect originates at the level of the spinal cord. The sedative
effect produced by dexmedetomidine has a different quality than that produced
by other intravenous anesthetics in that it more completely resembles a
physiologic sleep state through activation of endogenous sleep pathways.
Dexmedetomidine is likely to be associated with a decrease in cerebral blood
flow without signifi-cant changes in ICP and CMRO2. It has the
potential to lead to the development of tolerance and dependence.
B. Cardiovascular Effects
Dexmedetomidine
infusion results in moderate decreases in heart rate and systemic vascular
resistance and, consequently, a decrease in systemic blood pressure. A bolus
injection may produce a tran-sient increase in systemic blood pressure and
pronounced decrease in heart rate, an effect that is probably mediated through
activa-tion of peripheral α2 adrenoceptors. Bradycardia associated with
dexmedetomidine infusion may require treatment. Heart block, severe
bradycardia, and asystole have been observed and may result from unopposed
vagal stimulation. The response to anti-cholinergic drugs is unchanged.
C. Respiratory Effects
The
effects of dexmedetomidine on the respiratory system are a small to moderate
decrease in tidal volume and very little change in the respiratory rate. The
ventilatory response to carbon dioxide is unchanged. Although the respiratory
effects are mild, upper airway obstruction as a result of sedation is possible.
In addition, dexmedetomidine has a synergistic sedative effect when combined
with other sedative-hypnotics.
Clinical Uses & Dosage
Dexmedetomidine
is principally used for the short-term sedation of intubated and ventilated
patients in an ICU setting. In the operating room, dexmedetomidine may be used
as an adjunct to general anesthesia or to provide sedation, eg, during awake
fiberop-tic tracheal intubation or regional anesthesia. When administered
during general anesthesia, dexmedetomidine (0.5–1 mcg/kg load-ing dose over
10–15 minutes, followed by an infusion of 0.2–0.7 mcg/kg/h) decreases the dose
requirements for inhaled and injected anesthetics. Awakening and the transition
to the postoperative set-ting may benefit from dexmedetomidine-produced
sedative and analgesic effects without respiratory depression.
Related Topics