Chapter: Medical Microbiology: An Introduction to Infectious Diseases: Bacterial Genetics
Detection of Plasmids - Bacterial Genetics
Detection of Plasmids
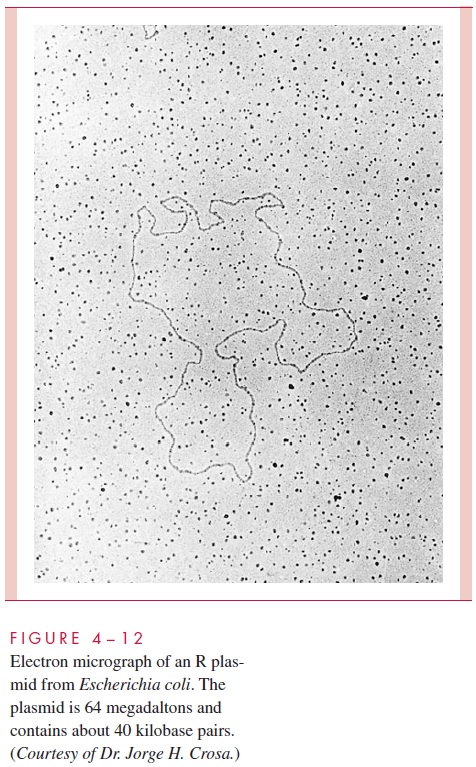
A number of physical, morphologic, and functional tests can be used to reveal the presence of plasmids in a bacterial population. The rapid transfer of characteristics, such as resis-tance to antimicrobics, from strain to strain or, alternatively, the rapid loss of such traits is a hallmark of plasmid-encoded characteristics. When several genetically distinct character-istics are transferred simultaneously in the laboratory into cells known not to have pos-sessed them previously, the evidence is very strong that a plasmid is responsible. Plasmids, including nonconjugative plasmids and those coding for no presently known trait, can be demonstrated directly by agarose gel electrophoresis. Electron microscopy can also be used to visualize plasmids, to measure the length of their DNA, and to see the forms they take on hybridiza-tion to other nucleic acid molecules (see Fig 4 – 12).
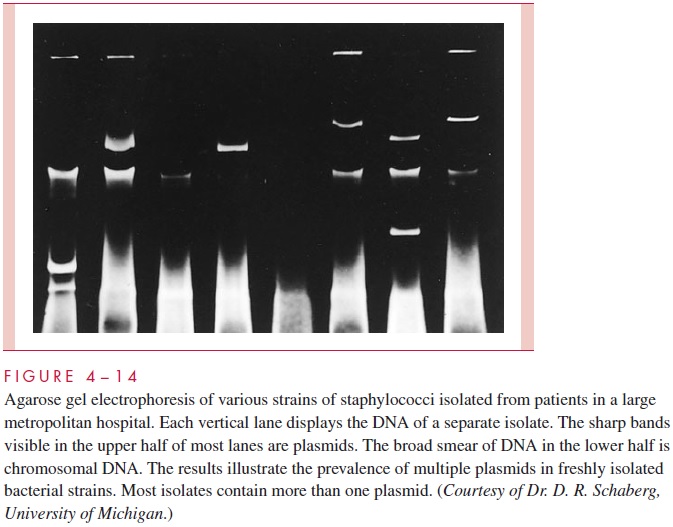
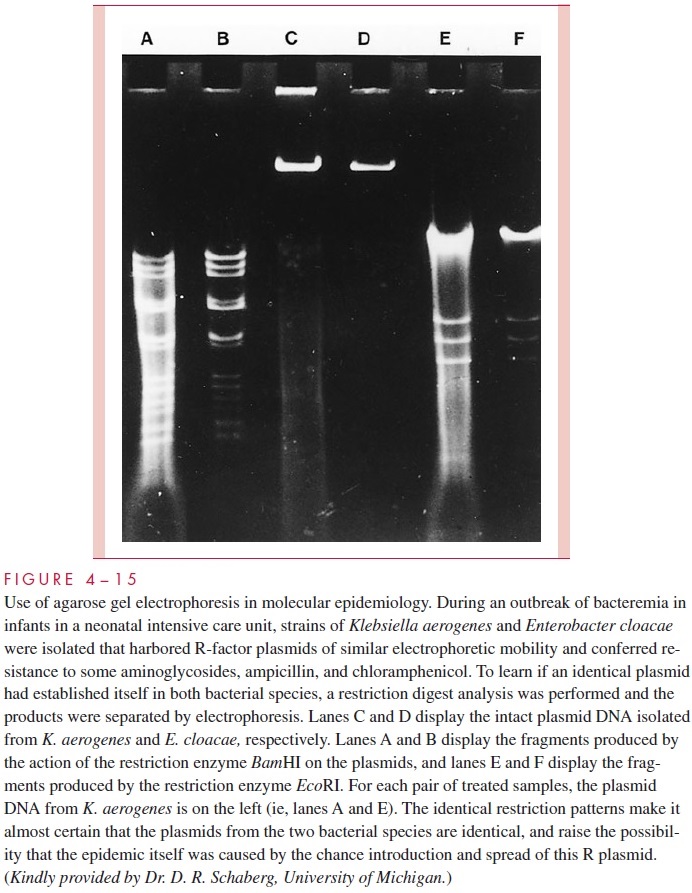
Bacterial plasmids, including R factors, have become valuable markers for comparing closely related strains of bacteria in epidemiologic studies. In outbreaks, spread of an epi-demic strain can sometimes be followed more easily and more accurately by monitoring the profile of plasmids carried in strains isolated from different patients than by using tra-ditional typing methods (Fig 4 – 14). This approach is particularly useful in studying out-breaks of nosocomial (hospital-acquired) infections. Likewise, the spread of an R plasmid between different species can be followed by showing that they carry an identical plasmid conferring the same pattern of antimicrobic resistance. The plasmid comparison can be carried one step further in specificity by cutting the plasmid DNA with specific restriction endonucleases (see next section) and examining the resulting fragments by agarose gel electrophoresis (Fig 4 – 15). Variations of this procedure enable even the spread of specific genes among a variety of plasmids to be detected.
Related Topics