Chapter: Civil : Construction Planning And Scheduling : Organization and Use of Project Information
Databases and Applications Programs
Databases
and Applications Programs
The usefulness of a database organization is particularly
evident in integrated design or management environments. In these systems,
numerous applications programs share a common store of information. Data is
drawn from the central database as needed by individual programs. Information
requests are typically performed by including pre- defined function calls to the
database management system within an application program. Results from one
program are stored in the database and can be used by subsequent programs
without specialized translation routines. Additionally, a user interface
usually exists by which a project manager can directly make queries to the
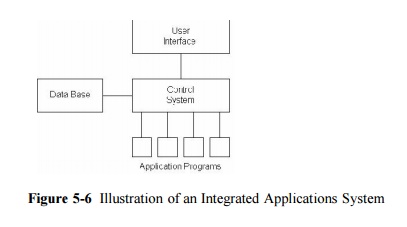
database. Figure
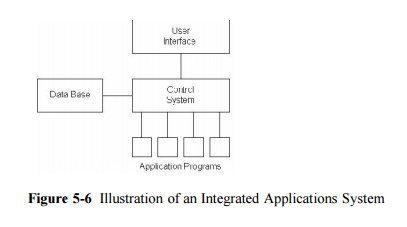
5-6
illustrates the role of an integrated database in this regard as the central
data store.
An architectural system for design can provide an
example of an integrated system. First, a database can serve the role of
storing a library of information on standard architectural features and component
properties. These standard components can be called from the database library
and introduced into a new design. The database can also store the description
of a new design, such as the number, type and location of individual building
components. The design itself can be composed using an interactive graphics
program. This program would have the capability to store a new or modified
design in the database. A graphics program typically has the capability to
compose numerous, two or three dimensional views of a design, to introduce
shading (to represent shadows and provide greater realism to a perspective),
and to allow editing (including moving, replicating, or sizing individual
components). Once a design is completed and its description stored in a database,
numerous analysis programs can be applied, such as:
z structural analysis,
z daylight contour programs to produce plots of available
daylight in each room, z a heat loss computation program
z area, volume and materials
quantities calculations.
Production
information can also be obtained from the integrated system, such as:
z dimensioned plans, sections and elevations, z component
specifications,
z construction detail specifications, z electrical layout,
z system isometric drawings,
z bills of quantities and
materials.
The advantage of an integrated system of this sort
is that each program need only be designed to communicate with a single
database. Accomplishing appropriate transformations of data between each pair
of programs would be much more difficult. Moreover, as new applications are
required, they can be added into an integrated system without extensive
modifications to existing programs. For example, a library of specifications
language or a program for joint design might be included in the design system
described above. Similarly, a construction planning and cost estimating system
might also be added.
The use of integrated systems with open access to a database
is not common for construction activities at the current time. Typically, commercial
systems have a closed architecture with simple datafiles or a
"captive," inaccessible database management system. However, the
benefits of an open architecture with an accessible database are considerable
as new programs and requirements become available over time.
Example
5-2: An Integrated System Design
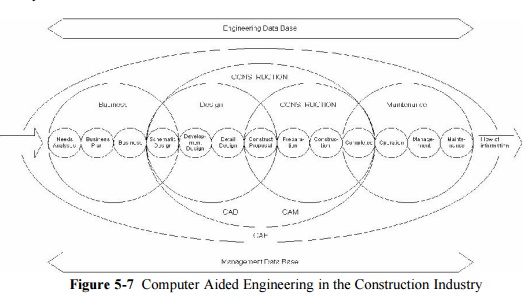
As an example, Figure 14-7 illustrates the computer aided
engineering (CAE) system envisioned for the knowledge and information-intensive
construction industry of the future. In this system, comprehensive engineering
and "business" databases support different functions throughout the
life time of a project. The construction phase itself includes overlapping
design and construction functions. During this construction phase, computer
aided design (CAD) and computer aided manufacturing (CAM) aids are available to
the project manager. Databases recording the "as-built" geometry and
specifications of a facility as well as the subsequent history can be
particularly useful during the use and maintenance life cycle phase of the
facility. As changes or repairs are needed, plans for the
facility
can be accessed from the database.
Related Topics