Chapter: Power System Analysis : Stability Analysis
Critical clearing angle and critical clearing time in transient stability
CRITICAL CLEARING ANGLE AND CRITICAL CLEARING TIME IN TRANSIENT STABILITY.
If a fault occurs in a system, δ begins to increase under the influence of positive accelerating power, and the system will became unstable If δ becomes very large. There is a critical angle within which the fault must be cleared if the system is to remain stable and the equal-area criterion is to be satisfied. This angle is known as the critical clearing angle. Consider the system of Fig. 11.9 operating with mechanical input Pi at stady angle δ0.(Pi=Pe) as shown by the point ‘a’ on the power angle diagram of Fig 11.10.
Now if a three phase short circuit occurs at the point F o the outgoing radial line, the terminal voltage goes to zero and hence the electrical power output of the generator instantly reduces to aero, i.e., Pe = 0 and the state point drops to ‘b’. The acceleration area A1 starts to increase while the state point moves along bc. At time tc corresponding clearing angle δo the fault is cleared by the opening of the line circuit breaker. tc is called clearing time and δe is called clearing angle. After the fault is cleared, the system again becomes healthy and transmits poer Pe = Pmaxsin δ, i.e., the state point shit to ‘d’ on the power angle curve. The rotor now decelerates and the decelerating area A2 begins to increase while the state point moves along de.
For stability, the clearing angle, δo must be such that area A1 = area A2.
Expressing area A1 = area A2 mathematically, we have
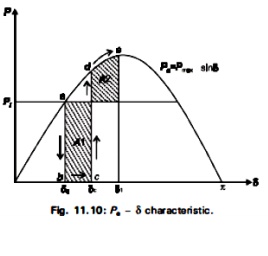
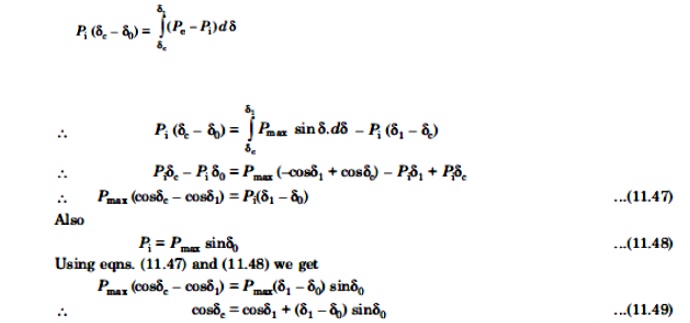
To reiterate, with reference to Fig. 11.10, the various angle in eqn.(11.49) are δe = clearing angle; δ0 = initial poer angle; and δ1 = power angle to which the rotor advances (or overshoots) beyond δe.
In order to determine the clearing time, we re-write eqn.(11.20), with Pe=0, since we have a three phase fault,

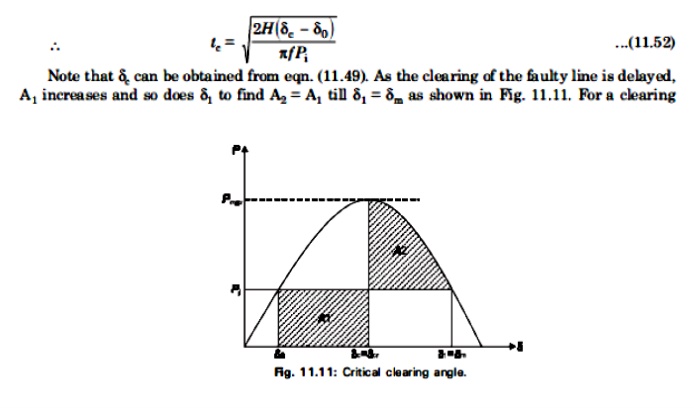
Angle (or clearing time) larger than this value, the system would be unstable. The maximum allowable value of the clearing angle and clearing time for the system to remain stable are known as critical clearing angle and critical clearing time respectively.
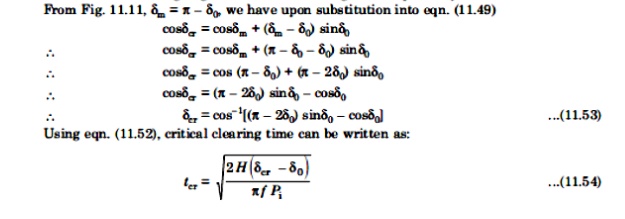
Related Topics