Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 8 : Periodic Classification of Elements
Corrosion
CORROSION
It is the gradual
destruction of metals by chemical or electrochemical reaction with the
environment. It is a natural process which converts a metal into its oxide,
hydroxide or sulphide so that it loses its metallic characteristics.
Rusting
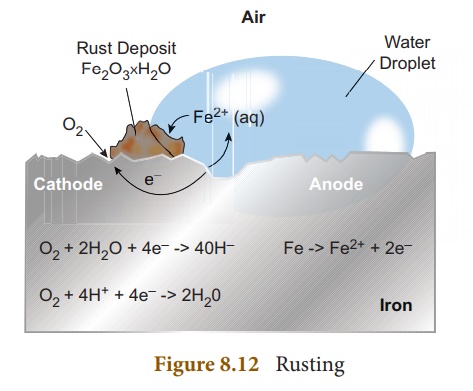
Rust is chemically known
as hydrated ferric oxide (it is formulated as Fe2O3.xH2O).
Rusting results in the formation of scaling reddish brown hydrated ferric oxide
on the surface of iron and iron containing materials.
1. Types of Corrosion
i. Dry Corrosion or
Chemical Corrosion: The corrosive action in the absence of moisture is called dry
corrosion. It is the process of a chemical attack on a metal by a corrosive
liquids or gases such as O2, N2, SO2, H2S
etc. It occurs at high temperature. Of all the gases mentioned above O2
is the most reactive gas to impart the chemical attack.
ii. Wet Corrosion or
Electrochemical Corrosion: The corrosive action in the presence of moisture is called
wet corrosion. It occurs as a result of electrochemical reaction of metal with
water or aqueous solution of salt or acids or bases.
2. Methods of preventing corrosion Alloying:
i. Alloying: The metals can be alloyed to prevent the process of corrosion.
E.g: Stainless Steel
ii. Surface Coating: It involves application
of a protective coating over the metal. It is of the following types:
a) Galvanization: It is the process of coating
zinc on iron sheets by using electric current.
b) Electroplating: It is a method of
coating one metal over another metal by passing electric current.
c) Anodizing: It is an electrochemical
process that converts the metal surface into a decorative, durable and
corrosion resistant. Aluminium is widely used for anodizing process.
d) Cathodic Protection: It is the method of controlling
corrosion of a metal surface protected is coated with the metal which is easily
corrodible. The easily corrodible metal is called Sacrificial metal to act as
anode ensuring cathodic protection.
Related Topics