Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XI first year 11th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Corals - reef builders - ECONOMIC ZOOLOGY
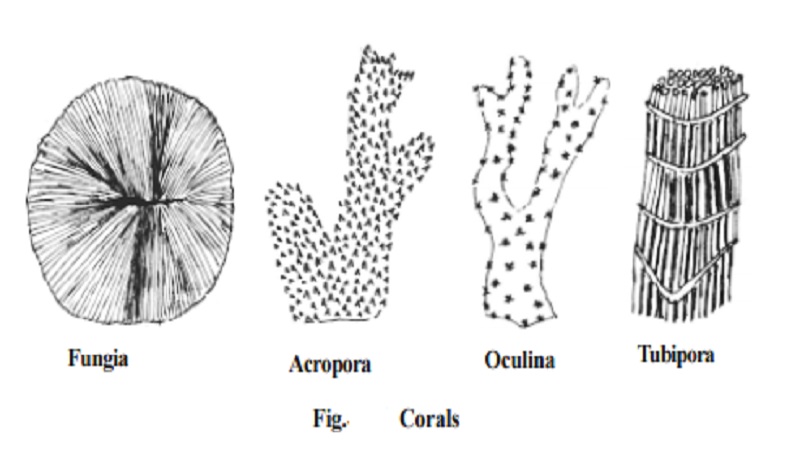
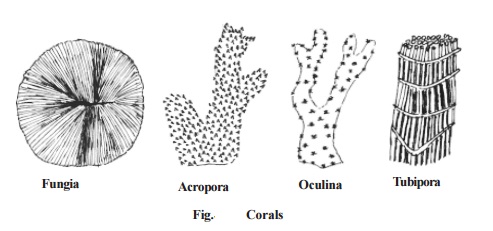
Corals - reef builders -
Most of us know about corals and are not familiar with their biology. Coral rocks are actually the skeletal remains, primarily of calcium carbonatesecreted by living coral polyps. The coral organisms belong to the phylum :
Coelenterata.
All reef building corals live as large colonies. Reef corals are typically shy, nocturnal feeders. During the day, polyps are withdrawn into skeletal cups and the corals appear more or less lifeless. But at night time the whole reef magically comes to life and coral polyps stretch out their tentacles, prob-ing the waters for food. The reef looks like a field of flowers.
Reef forming corals grow only in shallow, tropical seas where the temperature of the water never falls below 20o c. Only in warmer waters, the coral polyps can extract calcium from the sea water and deposit it as calcium carbonate in their skeletons. Corals thrive only in crystal clear water.
Small plants like Zooxanthella living in the coral tissue contribute to the yellow, brown and green colours of some reef forming corals. The brighter red and orange colours are created by pigment cells in the body wall.
Formation of coral reefs
Corals are best known for the massive rocky reefs they build in trop-ics. The corals spread by producing vast number of minute ciliated larvae calledPlanulae, through sexual reproduction. These larvae initially lead a free swimming life. Later they settle on rocks and start new colonies of pol-yps by repeated fission or budding. A coral reef is thus a result of the activity of millions of coral polyps over several thousand years.
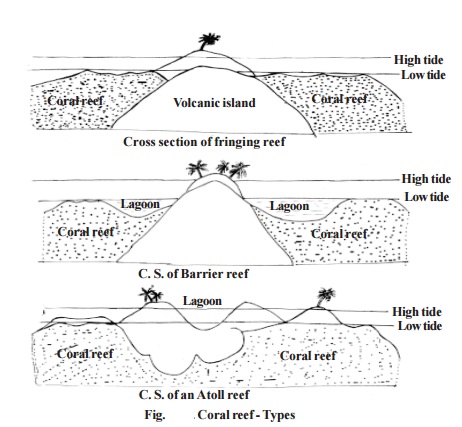
Coral reefs are of three types namely, Fringing reefs, Barrier reefs and Atolls. In India coral reefs occur in the Lakshadweep, Andaman and Nicobar Islands and in the south east-coast.
Fringing reefs form shallow shelves in shallow waters at or near the shore of the mainland or around offshore Islands. At the southern end of Indian peninsula, this type is seen as a chain of well developed reefs starting from Rameshwaram Island and extending beyond Tuticorin. They are also present in the Gulf of Kutch on the west coast of India.
Barrier Reefs are situated away from the coast and form off-shore break waters parallel to the coasts or isolated islands. The famous Great Barrier reef of North Eastern Australia which is 2012 kilometres long, is the largest of its kind.
Atolls consist of a ring shaped reef, encircling a shallow lagoon which is connected to the outside by an opening. Hawaii and Carribian Islands are famous for Atolls.
Economic importance
Some corals are highly priced for their decorative value. Precious corals like Corallium nobile ( = C . rubrum ) are used in jewellery and ornaments. Corals are also important in building the coral reefs and islands, some of which are used as habitation by human and other animals. The organ pipe coral(Tubipora) is used in indigenous system of medicine in South In-dia.
Coral skeletons especially of species like porites are used in as building construction and for metalling their roads. Corals serve as raw materials for the preparation of lime mortar and cement because of their calcium carbonate content. Some older coral lime stones are rich in magne-sium, hence they are of great value in making cement. Coral skeletons act as natural barriers against sea erosion and cyclonic storms. Old reefs have long served as sea bird sanctuaries and have collected huge deposits of bird drop-pings (guano).
Coral reefs provide a unique habitat for large and diverse variety of organisms. The richness of the invertebrate fauna and the complex structure of the coral reefs have provided opportunities for the evolution of a number of fishes associated with coral reefs.
In several countries Fringing reef, Barrier reef and Atolls are helping in the tourism industry.
Beneficial animals
The animals contributing to our economy and welfare are known as beneficial animals. Many animals provide us with nutritious food like meat and milk, clothing materials like silk and wool and the luxurious items like pearls and corals. The silk worms, the honey bees, the lac insects, fowls, fishes, prawns and crabs belong to this category.
ECONOMIC ZOOLOGY
Since time immemorial, human beings have used animals for food and other purposes. While some animals are very useful to mankind certain others cause loss to the economy of man. Though every organisms has its own im-portance in nature, some of them such as a few mammals, birds, fishes, prawns and insects have become valuable. Some pests are competitors of human be-ings for natural resources and food. Thus a study of economically important animals will always be useful.
Related Topics