Chapter: Obstetric and Gynecological Nursing : Anatomy of Female Pelvis and the Fetal Skull
Contents of the pelvis cavity
Contents of the pelvis cavity
1. The bladder
The bladder is the urinary reservoir which stores the urine until it is
convenient for it to be voided.
Position:- In the non-pregnant female,
the bladder liesimmediately behind the symphysis pubis and infront of the
uterus and vagina. The bladder when empty is of simillar size to the uterus but
when full of urine it becomes, much larger. Its capacity is around 600ml but it
is capable of holding more, particularly under the influence of pregnancy
hormones.
2. The Ureters
The tubes which convey the urine from the
kidneys to the bladder are the ureters.
Function – They assist the passage of the
urine by themuscular peristaltic action of their wall.
The upper end is funnel shaped and merges in to the pelvis of the kidney where the urine is received from the renal tubules.
3. Urethra
The female urethra is about 4cm long and courses
downward and anterior to the bladder neck. It terminates in the vestibule of
the vagina between the labia minora and about 2.5cm posterior to the glans of
the clitoris.
4. The uterus
The uterus is a hallow, muscular, pear shaped organ situated in the true
pelvis.
Function:-exists to shelter the fetus during
pregnancy. Ifprepares for this possibility each month and following pregnancy
it expels the uterine contents.
Position - It leans forward, which is
known as anteversion, itbends forwards on itself, which is known as anteflexion
Relation- anteriorly the bladder and
posteriorly rectum
Inferior - Below the uterus is the vagina
Superior - above the uterus lie the
intestine
Lateral-on both sides of the walls are
the broad ligaments, thefallopian tubes and the ovaries.
Supports - supported by the pelvic floor
and maintained inposition by several ligaments. Ligaments are;
Pertonial ligament ƒ Broad ligament
i.
Genito inguinal ligament
a.
Round ligament
ii. Ligaments formed by pelvic fascia
a. Transverse cervical ligament
b.
Utero sacral ligament
Structures - the non pregnant uterus 7.5 cm
long, 5cm wideand 2.5cm in depth, each wall being 1.25 cm thick. The Cervix
forms the lower third of the uterus.
Parts of the uterus
·
The body or corpus - the upper 2/3 of the uterus and is the greater
part.
·
The fundus - the domed upper wall between the insertions of the
fallopian tubes.
·
The cornua - are the upper outer angle of the uterus where the fallopian
tubes join.
·
The cavity - is a potential space between the anterior and posterior
walls.
·
The isthmus - is a narrow area between the cavity and the cervix, which
is 7mmlong. It enlarges during pregnancy to form the lower uterine segment.
·
The cervix or neck - protrudes in to the vagina.
·
The internal os (mouth) is the narrow opening between the isthmus and
the cervix
·
The external os is a small round opening at the lower end of the cervix.
Layers:-The uterus has three layers, of
which the middlemuscle layer is by far the thickest.
The endometrium: - forms a lining of ciliated epithelium(mucous memberane) on a base of connective tissue or stroma. It is constantly changing in thickness through out the menustral cycle.
The myomatrium or muscle coat: -
is thick in the
upper partof the uterus and is sparser in the isthmus and cervix. It has three
parts: Outer longitudinal, middle oblique and inner circular.
The perimetrium is a double serous memberane,
anextension of the peritoneum, which is dragged over the uterus.
Blood supply – The uterine artery arrives at
the level of thecervix and is a branch of the internal iliac artery. The blood
drains through corresponding veins.
Nerve supply – from the autonomic nervous
system,sympathetic and para smpathetic via pelvic plexus.
5. Fallopian tube or uterine tube
Function-Propels the ovum towards the
uterus
i.
Receives the spermatozoa as they travel up wards provides a site for
fertilization
ii.
It supplies the fertilized ovum with nutrition during its continued
journey to the uterus
Position - extend laterally from the
cornea of the uterustowards the side walls of the pelvis
Supports - are held in place by their
attachment to the uterus.
Structure - Each tube is 10cm long. It has
four portions
·
The interstitial portion is 1.25cm long and lies with in the wall of the
uterus. Its lumen is 1 mm wide.
·
The isthmus is another narrow part which extends for 2.5cm from the
uterus
·
The ampoule is the wider portion where fertilization usually occurs. It
is 5 cm long.
·
The infundibulum is the funnel - shaped fingered end which is composed
of many process known as fimbriae. One fimbria is elongated to form the ovarian
fimbria which is attached to the ovary.
6. The ovaries
Function: - produce ova and the hormones
estrogen andprogesterone
Position: - they are attached to the back of
the broadligamentnear the fimbriated end of the fallopian tube.
Blood supply: - Supplied by the ovarian
arteries and drainsby the ovarian veins.The right ovarian vein join the
inferior venecava, but the left returns its blood to the left renal vein.
Lymphatic drainage is to the lumbar glands
Nerve supply is from the ovarian plexus.
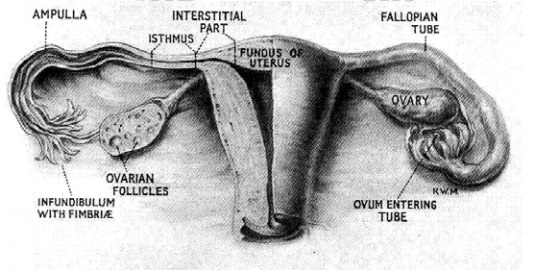
Figure 7. Anterior view of female reproductive organs
Related Topics