Chapter: Digital Electronics : Combinational Circuits
Code Converters
CODE CONVERTERS
Binary-to-Gray
The table that follows shows natural-binary numbers (upto 4-bit) and corresponding gray codes.
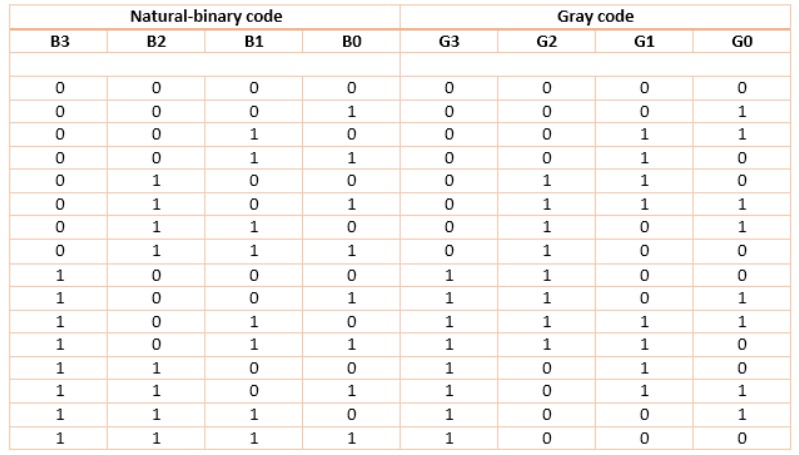
Looking at gray-code (G3G2G1G0), we find that any two subsequent numbers differ in only one bit-change.
The same table is used as truth-table for designing a logic circuitry that converts a given 4-bit natural binary number into gray number. For this circuit, B3 B2 B1 B0 are inputs while G3 G2 G1 G0 are outputs.
K-map for the outputs:
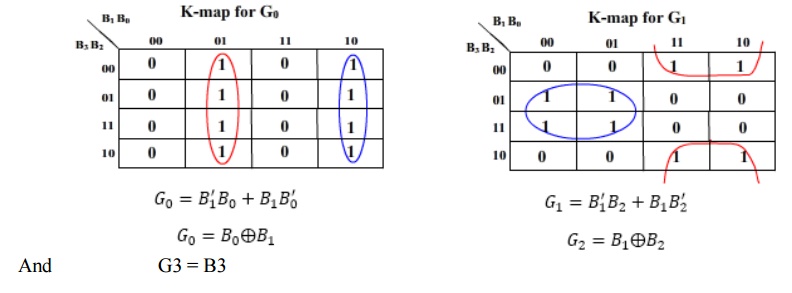
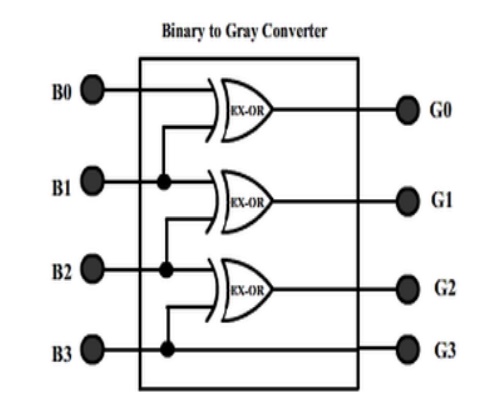
So that’s a simple three EX-OR gate circuit that converts a 4-bit input binary number into its equivalent 4-bit gray code. It can be extended to convert more than 4-bit binary numbers.
Gray-to-Binary
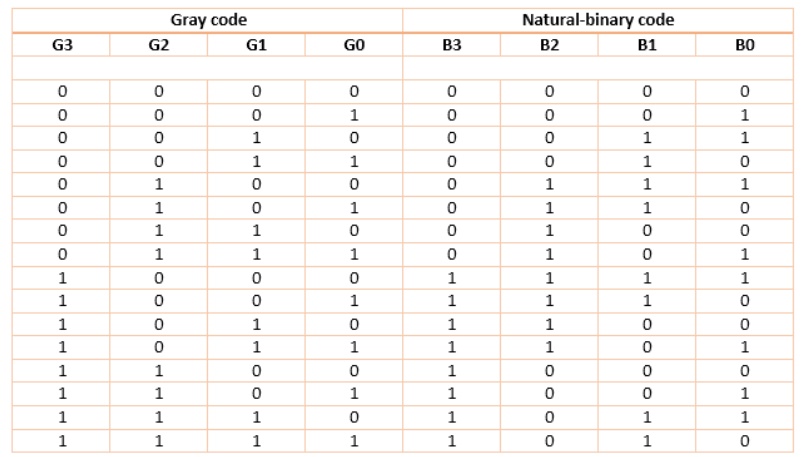
Once the converted code (now in Gray form) is processed, we want the processed data back in binary representation. So we need a converter that would perform reverse operation to that of earlier converter. This we call a Gray-to-Binary converter.
The design again starts from truth-table:
Then the K-maps:
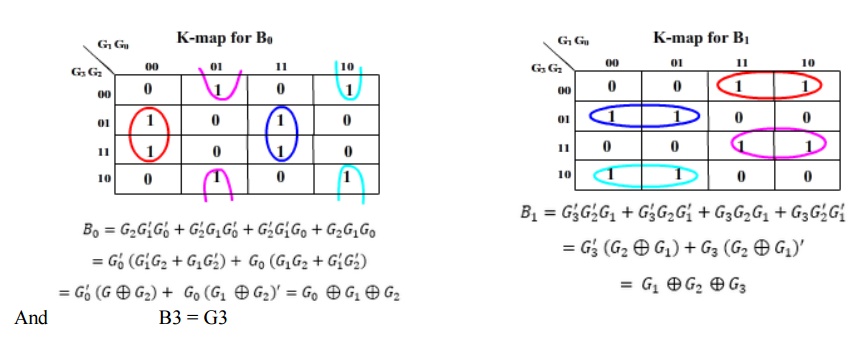
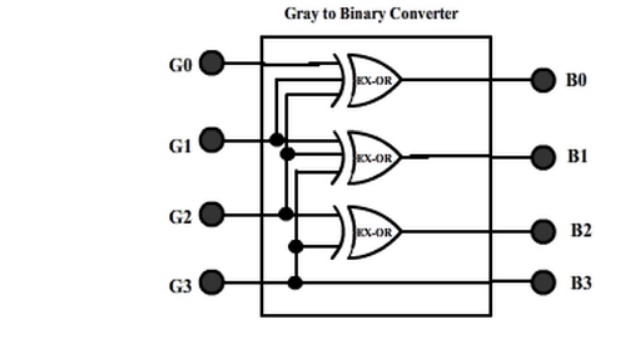
The realization of Gray-to-Binary converter is
Related Topics