Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Organic Inorganic Physical Chemistry Higher secondary school College Notes
Co-ordinate-covalent bonding or Dative bonding
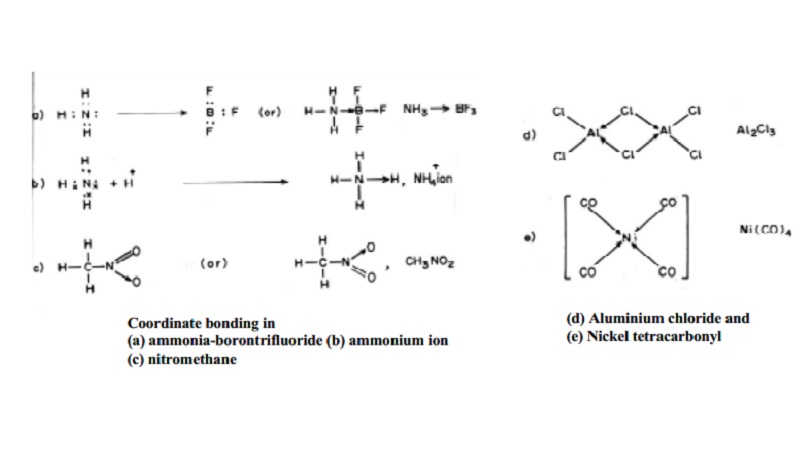
Co-ordinate-covalent
bonding or Dative bonding
The electron contributions of combining atoms in
a covalent bond are generally equal. In each shared pair of electrons one
electron is contributed from each atom of the bond. However in some bond
formation, the whole of the shared pair of electrons comes from only one of the
combining atoms of the bond, which is to referred as the donor atom. The other
atom which does not contribute the electron to the shared pair but tries to
pull the pair of electron towards itself is called as the acceptor atom. The bond
thus formed is between the donor and acceptor atoms is called as the co-ordinate or co-ordinate - covalent or
dative bond.
A coordinate bond is showed as an arrow which
points from the donor to the acceptor atom. In some cases, the donated pair of
electron comes from a molecule as a whole which is already formed to an already
formed acceptor molecule as a whole.
For Example, coordination bond between H3N: and
BF3 molecules. The molecule, ammonia (donor) which gives a pair of electron
(lone pair) to BF3 molecule which is electron deficient (acceptor) which has an
empty orbital to accommodate the pair of electrons. Thus a dative bond is
formed and the molecule as a whole is represented as H3N -- > BF3 (Fig. a).
When
Proton is added to ammonia, a pair of electron is donated by nitrogen to proton
and then proton shares the electron pair to form coordinate covalent bond.

Similarly in (NH4Cl) ammonium chloride, covalent - coordinate bond
exists in NH4+ ion only and Cl- ion exists as it is.
Few examples of covalent - coordinate bond :
In nitro
methane (CH3 - NO2), one of the N-O-bond exists in a
covalent coordinate type.
Aluminum chloride Al2Cl6
(dimeric form)
Lone pairs of electron from chlorine are donated to electron deficient
aluminium atoms in such a way that dimers of AlCl3 are formed easily
(Fig. d). The two chlorine atoms act as bridge to link the two Aluminium atoms.
In some
complex ion formations, if the central transition metal-ion has empty `d'
orbitals then lone pair of electrons from neutral molecules or anions are
donated resulting in the formation of coordination bonds. Example : In Nickel
tetracarbonyl, the four bonds between central Ni atom and the carbonyl ligands
are mainly covalent -coordinate type. This complex exists in square planar
geometry.
Related Topics