Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Rails
Classification of Rail Flaws
Classification of Rail Flaws
Depending upon the nature and extent of internal flaws, traffic density, and speed on the section, the defects noticed by rail flaw detection methods have been classified into three major categories, i.e., IMR, REM, and OBS.
IMR defects A defect that is serious in nature and can lead to sudden failure is classified as IMR. Immediately after detection, clamped fish plates should be provided for the defective portions and a speed restriction of 30 kmph imposed till the IMR rail is removed by a sound-tested rail piece of not less than 6 m. A watchman should be posted till the clamped fish plates are provided to avoid any mishaps. IMR stands for immediate removal.
REM defects These are the type of defects that warrant early removal of the rail from the track. These defects are marked with red paint. REM stands for remove.
OBS defects These are defects that are not so serious. The rail need not be removed in such cases but should be kept under observation. These defects are marked with yellow paint. OBS stands for observe. OBS defects have been further classified as OBS (E) and OBS (B). An OBS defect located within the fish-plated zone is designated OBS (E). Similarly, an OBS defect on major bridges and up to 100 m on their approaches is designated OBS (B).
In the case of the need-based concept of ultrasonic testing (explained in Section 6.8.6), there are only two types of defects, IMR and OBS. However, if the defects occur at welded joints, they are called IMR (R) and OBS (W) defects.
The actions to be taken upon the detection of defective rails are summarized in Table 6.10.
Table 6.10 Actions to be taken upon the detection of defective rails
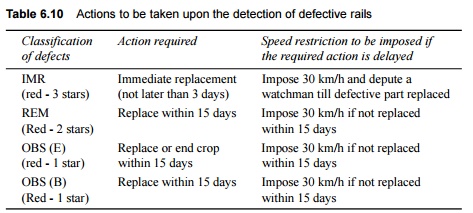
In the case of OBS rails other than OBS (E) and OBS (D), permanent way inspector (PWI) should observe each OBS location with a magnifying glass and duly record his observations once a month, to see if the crack has developed any further, in which case the same action as for REM defects should be taken. The PWI should maintain sleepers, fittings, and the ballast at such locations in sound condition. The assistant engineer should also test-check some of the OBS locations and record his observations during his monthly push trolley inspection of each section.
Related Topics