Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Patients With Diabetes Mellitus
Classification of Diabetes
Classification of Diabetes
There
are several different types of diabetes mellitus; they may differ in cause,
clinical course, and treatment. The major classifi-cations of diabetes are:
•
Type 1 diabetes (previously referred to
as insulin-dependentdiabetes mellitus)
•
Type 2 diabetes (previously referred to
as non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus)
•
Gestational diabetes mellitus (ADA, Expert
Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus, 2003)
•
Diabetes mellitus associated with other conditions
or syndromes
OVERVIEW
The
terms “insulin-dependent diabetes” and “non-insulin-dependent diabetes” and
their acronyms (IDDM and NIDDM, respectively) are no longer used because they
have resulted in clas-sification of patients on the basis of the treatment of
their diabetes rather than the underlying etiology. Use of Roman numerals (type
I and type II) to distinguish between the two types has been changed to type 1
and type 2 to reduce confusion (ADA, Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and
Classification of Diabetes Mel-litus, 2003).Approximately 5% to 10% of people
with diabetes have type 1 diabetes, in which the insulin-producing pancreatic
beta cells are destroyed by an autoimmune process. As a result, they produce
little or no insulin and require insulin injections to control their blood
glucose levels. Type 1 diabetes is characterized by an acute onset, usually
before age 30 (CDC, Diabetes Surveillance, 1999).
Approximately
90% to 95% of people with diabetes have type 2 diabetes (CDC, Data Factsheet,
2002), which results from decreased sensitivity to insulin (called insulin
resistance) and im-paired beta cell functioning resulting in decreased insulin
pro-duction (Quinn, 2001a). Type 2 diabetes is first treated with diet and
exercise. If elevated glucose levels persist, diet and exercise are
supplemented with oral hypoglycemic agents. In some individu-als with type 2
diabetes, oral agents do not control hyperglycemia, and insulin injections are
required. In addition, some individuals whose type 2 diabetes can usually be
controlled with diet, exercise, and oral agents may require insulin injections
during periods of acute physiologic stress (eg, illness or surgery). Type 2
diabetes occurs more among people who are older than 30 years and obese
(Diabetes Information Clearing House, 2001).
Diabetes
complications may develop in any person with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, not
only in patients who take insulin. Some patients with type 2 diabetes who are
treated with oral medica-tions may have the impression that they do not really have dia-betes or that they
simply have “borderline” diabetes. They may believe that, compared with
diabetic patients who require insulin injections, their diabetes is not a
serious problem. It is important for the nurse to emphasize to these
individuals that they do have
diabetes and not a borderline problem with sugar (glucose). Borderline diabetes
is classified as impaired glucose
tolerance(IGT) or impaired fasting
glucose (IFG) and refers to a condi-tion in which blood glucose levels fall
between normal levels and levels considered diagnostic for diabetes.
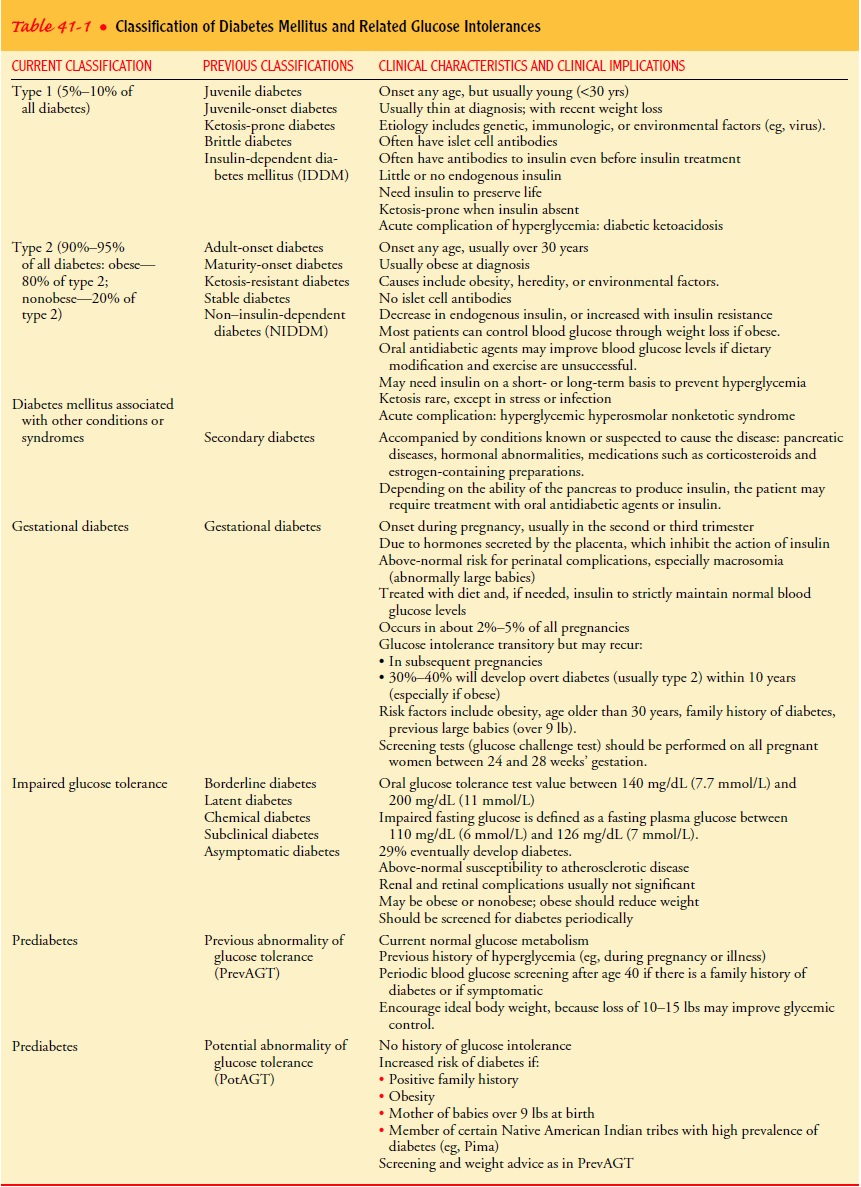
Table
41-1 summarizes the major classifications of diabetes, current terminology, old
labels, and major clinical characteristics. This classification system is
dynamic in two ways. First, research findings suggest many differences among
individuals within each category. Second, except for those with type 1
diabetes, patients may move from one category to another. For example, a woman
with gestational diabetes may, after delivery, move into the type 2 category.
These types also differ in their etiology, clinical course, and management.
Related Topics