Chapter: Medical Physiology: Female Physiology Before Pregnancy and Female Hormones
Chemistry of the Sex Hormones
Chemistry of the Sex Hormones
Estrogens. In the normalnonpregnantfemale, estro-gens are secreted in significant quantities only by the ovaries, although minute amounts are also secreted by the adrenal cortices. During pregnancy, tremendous quantities of estrogens are also secreted by the placenta.
Only three estrogens are present in significant quan-tities in the plasma of the human female: b-estradiol,estrone, and estriol, the formulas for which are shownin Figure 81–6. The principal estrogen secreted by the ovaries is b-estradiol. Small amounts of estrone are also secreted, but most of this is formed in the peripheral tissues from androgens secreted by the adrenal cortices and by ovarian thecal cells. Estriol is a weak estrogen; it is an oxidative product derived from both estradiol and estrone, with the conversion occurring mainly in the liver.
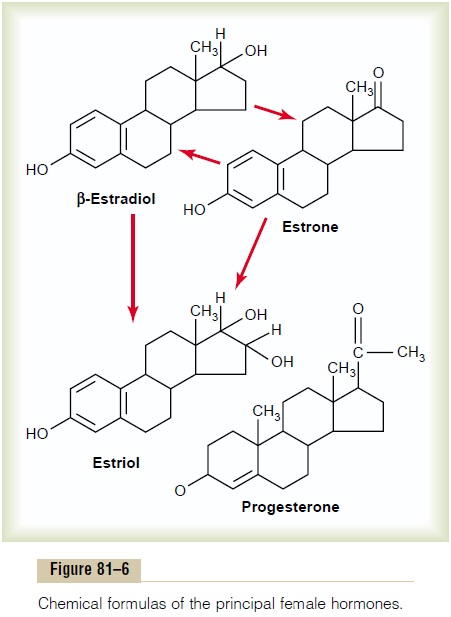
The estrogenic potency of b-estradiol is 12 times that of estrone and 80 times that of estriol. Consider-ing these relative potencies, one can see that the total estrogenic effect of b-estradiol is usually many times that of the other two together. For this reason, b-estradiol is considered the major estrogen, although the estrogenic effects of estrone are not negligible.
Progestins. By far the most important of the progestinsis progesterone. However, small amounts of another progestin, 17-a-hydroxyprogesterone, are secreted along with progesterone and have essentially the same effects. Yet, for practical purposes, it is usually reason-able to consider progesterone the only important progestin.
In the normal nonpregnant female, progesterone is secreted in significant amounts only during the latter half of each ovarian cycle, when it is secreted by the corpus luteum.
As we shall see, large amounts of progesterone are also secreted by the placenta during pregnancy, especially after the fourth month of gestation.
Synthesis of the Estrogens and Progestins. Note from thechemical formulas of the estrogens and progesterone in Figure 81–6 that they are all steroids. They are synthesized in the ovaries mainly from cholesterol derived from the blood but also to a slight extent from acetyl coenzyme A, multiple molecules of which can combine to form the appropriate steroid nucleus.
During synthesis, mainly progesterone and the male sex hormone testosterone are synthesized first; then, during the follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, before these two initial hormones can leave the ovaries, almost all the testosterone and much of the proges-terone are converted into estrogens by the granulosa cells. During the luteal phase of the cycle, far too much progesterone is formed for all of it to be converted, which accounts for the large secretion of progesterone into the circulating blood at this time. Also, about one fifteenth as much testosterone is secreted into the plasma of the female by the ovaries as is secreted into the plasma of the male by the testes.
Estrogens and Progesterone Are Transported in the Blood Bound to Plasma Proteins. Both estrogens and progesteroneare transported in the blood bound mainly with plasma albumin and with specific estrogen- and prog-esterone-binding globulins. The binding between these hormones and the plasma proteins is loose enough that they are rapidly released to the tissues over a period of 30 minutes or so.
Functions of the Liver in Estrogen Degradation. The liverconjugates the estrogens to form glucuronides and sul-fates, and about one fifth of these conjugated products is excreted in the bile; most of the remainder is excreted in the urine. Also, the liver converts the potent estrogens estradiol and estrone into the almost totally impotent estrogen estriol. Therefore, dimin-ished liver function actuallyincreases the activity of estrogens in the body, sometimes causing hyperestrinism.
Fate of Progesterone. Within a few minutes after secre-tion, almost all the progesterone is degraded to other steroids that have no progestational effect. As with the estrogens, the liver is especially important for this metabolic degradation.
The major end product of progesterone degradation is pregnanediol. About 10 per cent of the original prog-esterone is excreted in the urine in this form. There-fore, one can estimate the rate of progesterone formation in the body from the rate of this excretion.
Related Topics