Chapter: Mobile Networks : Cellular Wireless Network
Cellular Operation
CELLULAR OPERATION:
Cellular
network organization uses low power transmitter(100W or less).The areas are
divided into cells. Each cell is served by its own antenna and a base station
consisting of transmitter, receiver, and control unit.
There are
three basic devices they are:
·
A mobile station(MS)
·
A base transceiver Station(BS)
·
A Mobile Telecommunications Switching Office (MTSO)
Base
station include an antenna, a controller, and a number of receivers.
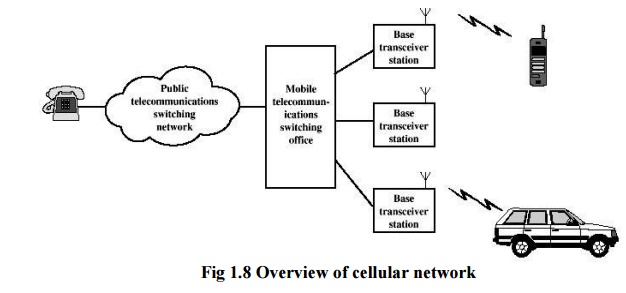
Base
station is at center of each cell. Base station is connected to MTSO. One MTSO
serve as multiple Base station. The link between MTSO to BS is by wire or
wireless.MTSO connects calls between mobile units and from mobile to fixed
telecommunications network .It assigns voice channel and performs handoffs and
monitors calls (billing).
Two
channels are available between mobile unit and BS, they are:
1. Control channel: They are used to exchange
information and perform setup and
maintaining calls. It establishes a relationship between Mobile unit and
nearest BS.
2. Traffic channel: It carries voice or data
connection between users.
Public
Land Mobile Network (PLMN) refer to a cellular network that has land and radio
based sections.
This
network consist of:
·
Mobile station (MS) is a device used for
communication over the network.
·
Base station transceiver (BST) is atransmitter/receiver
that are used to transmit/receive signals over the network.
·
Mobile switching center (MSC) is used to Sets up and maintain calls made
over the network.
·
Base station controller (BSC) which provides a
Communication between a group of BSTs and a single MSC is controlled by the BSC
·
Public switched telephone network (PSTN) Consist of
Section of the network that is land base.
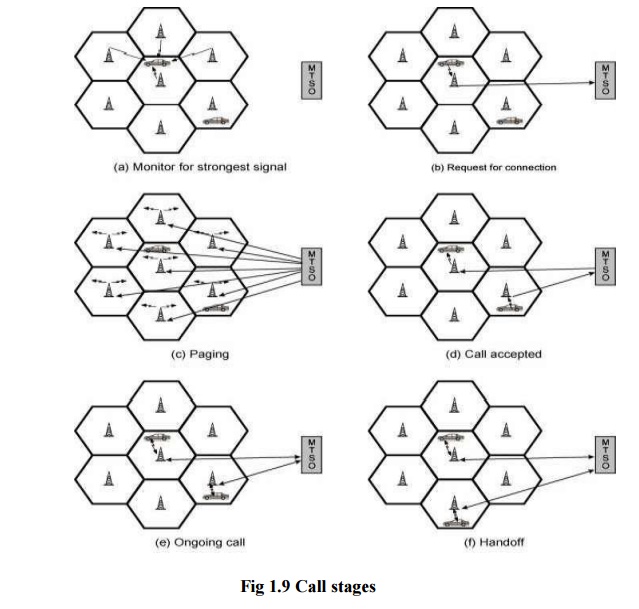
Steps in
MTSO controlled call connecting mobile units:
1. Mobile
unit initialization scans and choose strongest set up control channel
and automatically pick up a BS antenna of cell. Handshake is used to spot user
and register location. Scan is recurring to allow for movement of change of
cell.
2. Mobile
originated call check if the set up channel is free and Send number
on pre-selected channel.
3. In Paging
MTSO attempts to connect to mobile unit. Depending on called mobile number the
paging message will be sent to BSs. By using the setup channel Paging signal is
transmitted.
4. In call
accepted, the Mobile unit recognizes the number on the set up channel
and responds to BS which in turn send response to MTSO. Then the MTSO sets up a
circuit between calling and called BSs and select a available traffic channel
within cells and notifies BSs. The BSs notify mobile unit of channel.
5. In Ongoing
call the Voice/data is exchanged through respective BSs and MTSO.
6. If the
signal strength decreases as the mobile moves out of range from BTS it is
called handoff. And the
traffic channel changes to the one assigned to new BS.
Other
Functions:
1. Call
blocking: On mobile-initiated call stage, if all the traffic channels
are busy, the mobile tries again and again. After numeral retries, a busy tone
will be returned.
2. Call
termination: The User will hang up, MTSO is informed and the traffic
channels at two BSs are released.
3. Call
drop: If the BS cannot maintain a required signal strength then call
drop will occur and the traffic channel is dropped and MTSO informed.
4. Calls
to/from fixed and remote mobile subscriber: Here the
MTSO
connects to PSTN and can connect to mobile user and fixed subscriber
via PSTN. MTSO can also connect to remote MTSO via PSTN or via dedicated line.
Mobile Radio Propagation Effects: Signal
strength between BS and mobile unit is
strong enough to maintain signal quality at the receiver. Signal propagation
effects may interrupt the signal and causes error. This is called fading.
Power control:
Design
issues making it advantageous to include dynamic power control in cellular
systems.For effective communication, the power received must be sufficiently
above the background noise. It is advantageous to minimize the power in the
transmitted signal from the mobile. Thus it reduce co-channel interference,
save battery power and alleviate health concern.Types of power control:
Open-loop power control:
It
depends solely on mobile unit. There is no feedback from BS. Open loop is not
as accurate as closed loop, but it can react quicker to fluctuate in signal
strength.
Closed-loop power control:
Based on
performance metric the signal strength is adjusted in reverse channel.BS
makes power tuning decision and communication to mobile on control channel.
Traffic Engineering:
Traffic
engineering is a method of optimizing the performance of a telecommunication
network by vigorously analyzing, predicting and regulating the behavior of data
transmitted over that network. Traffic engineering is also known as tele
traffic engineering and traffic management. The method of traffic engineering
can be applied to networks of all kinds, together with the PSTN (public
switched telephone network), LANs (local area networks), WANs (wide area
networks), cellular telephone networks, proprietary business and the Internet
.For N simultaneous user capacity and L subscribers
L < N
– non-blocking system, L > N – blocking system.
Traffic Intensity:
Load
accessible to a system:
A=l h
Where
l -mean rate of calls attempted per unit time
h -mean holding time per successful
call
A -average number of calls arriving
during average holding period, for normalized
Related Topics