Non Communicable Diseases - Causes, Risk factor, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, Management - Cardio Vascular Disorders | 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 3 : Non Communicable Diseases
Cardio Vascular Disorders
CARDIO
VASCULAR DISORDERS
Hypertension
Acute Myocardial
Infarction
Anaemia
1. Hypertension
A normal blood pressure
reads as 120/80 where 120 denotes the systolic pressure and 80 denotes the
diastolic pressure. When the value of blood pressure is 140/90 and above, then
it is called as high blood pressure or hypertension.
Causes
·
Smoking
·
High blood cholesterol
·
Over weight
·
High salt intake
·
Alcohol intake
·
Renal disorder
·
Endocrine disorder
·
Vascular disorder
·
Neurological disorder
·
Problems with pregnancy
·
Acute stress
Risk factors
• Non modifiable![]()
Family history
Gender, age
• Modifiable
Stress
Obesity
Substance abuse
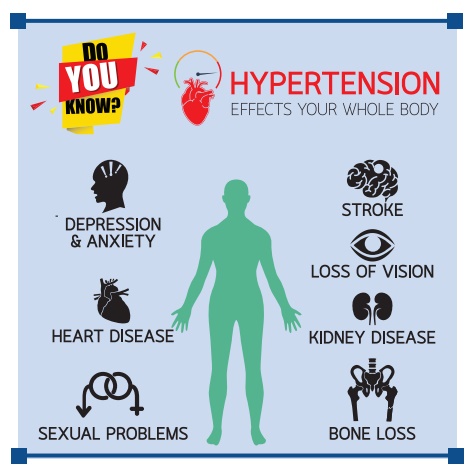
Signs & Symptoms
·
Fatigue
·
Head ache
·
Shortness of Breath
·
Giddiness
·
Palpitation
·
Ringing in the ears
·
Epistaxis
·
Heart failure
·
Cardiac pain
·
Coronary thrombosis
·
Stroke
·
Renal failure
Investigations
·
History collection
·
Physical examination
·
ECG
·
Renogram, renal arteriogram
·
Laboratory study of blood and urine
·
Fundoscopic examination
Management
Medical Management
·
Diuretics
·
Beta blockers
·
Calcium antagonist
Dietary management
·
Reduction of weight
·
Restrict fat intake
·
Restrict sodium intake
·
Avoid consumption of alcohol, caffeine
·
Avoid smoking
·
Encourage the patients to take food contain potassium
Relaxation technique:
·
Transcendental meditation
·
Yoga
·
Progressive muscle relaxation
Psychotherapy

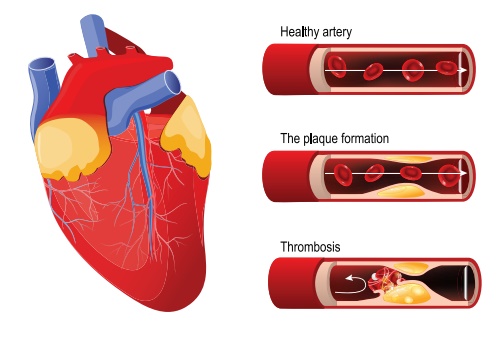
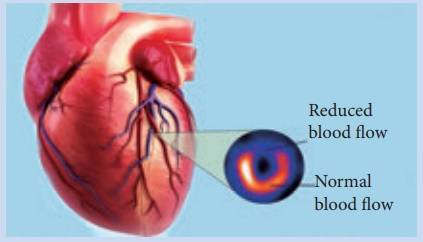
2. Acute Myocardial Infarction
Myocardial infarction
refers to a dynamic process by which one or more regions of myocardium
experience prolonged decrease in oxygen supply because of insufficient coronary
blood flow causing necrosis of tissue.
Causes
·
Occlusion of a coronary artery
·
Streneous physical activity
·
Emotional stress such as anger
·
Exposure to cold
·
Thrombus formation
Signs & Symptoms
·
Chest pain radiating to one or both arms, neck and back
·
Dyspnea or orthopnea
·
Shortness of breath
·
Anxiety
·
Systolic blood pressure less than 80 mm of Hg
·
Tachycardia or bradycardia
·
Weakness, cold, sweat, pallor
·
Palpitation
·
Peripheral cyanosis
·
Nausea or vomiting
Investigations
·
12 lead ECG
·
Echocardiography
·
Trop-I
·
serum CPK-MP and (CPK)
·
Lipid Profile
·
ESR
Management
Medical Management
·
Nitrates – help to relieve pain
·
Calcium channel blockers – prevents vasodilation
·
Beta-blockers
·
Morphine-act as analgesics and sedatives
·
Oxygen supply
·
Heparin therapy
·
Antiplatelet therapy
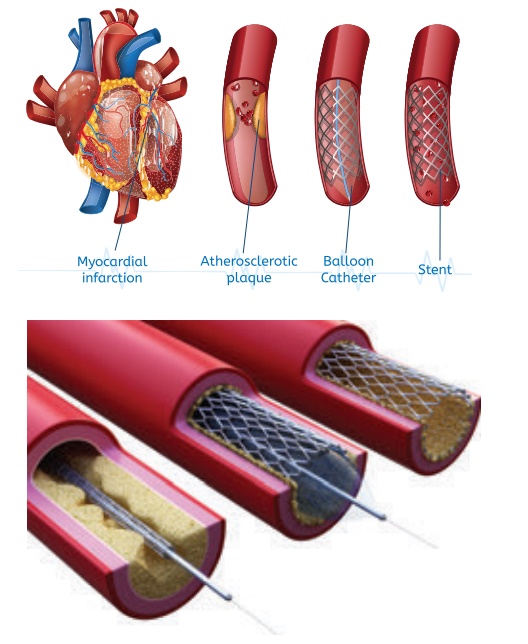
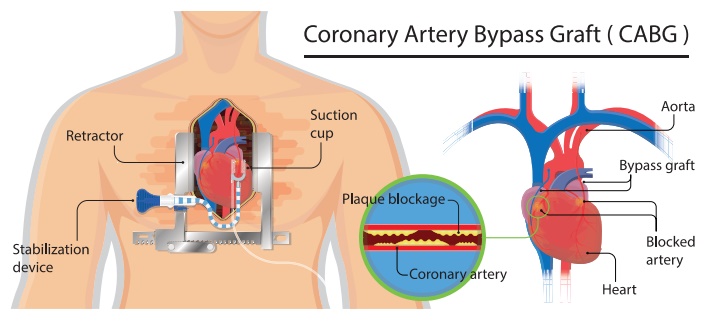
Sugical Management
·
Angioplasty
·
CABG
Nursing Management
·
Provide proper rest![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
·
Assess for previous health history regarding allergic medications,
trauma etc
·
Reassure the patient
·
Monitor the vital signs
·
Administer thrombolytic therapy
·
Administer oxygen as required
·
Assess the characteristic of chest pain including location,
duration, and quality.
·
Maintain intake output chart
·
Instruct to avoid alcohol, smoking and physical activity
·
Educate the patient to change life style and rehabilitation
Complication
·
Pulmonary embolism
·
Pericarditis
·
Shock
·
Mitral incompetence
·
Heart failure
·
Rupture of the heart
·
Phlebothrombosis
·
Angina pectoris
3. Anaemia
Anaemia is a condition
in which there is a reduction in the number of red blood cells and a deficiency
of haemoglobin resulting in decreased oxygen-carrying capacity.
Causes
·
Blood loss related to trauma
·
Decreased production of platelets.
·
Increased destruction of platelets
·
Decreased number of clotting factor.
·
Impairment of RBC production due to nutritional deficiency, (e.g
Iron deficiency, folic deficiency,
·
Vitamin B12 deficiency, Vitamin B6 deficiency).
·
Decreased erythrocyte production, bone narrow depression.
·
Increased erythrocyte destruction due to
i. Extrinsic factors
Drugs and chemicals
Infection
Antibody reaction
ii. Intrinsic factors
Abnormalities of RBC membrane
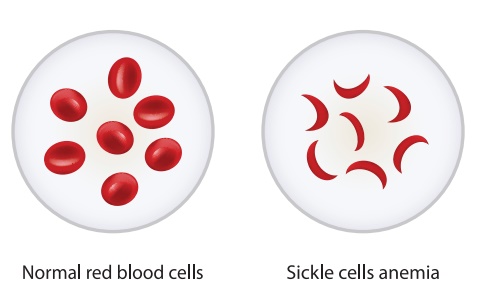
Abnormal haemoglobin synthesis sickle cell, disease, thalasemia
syndrome
Pathophysiology
RBCs and haemoglobin are
normally formed at the same rate at which they are destroyed.
Whenever formation of
RBCs or haemoglobin is decreased or their destruction is increased, anaemia
results.
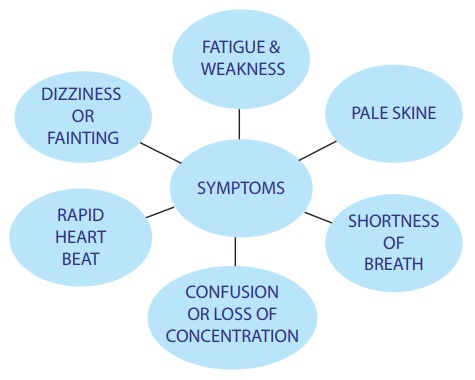
Signs and Symptoms
Diagnosis
·
Complete blood count
·
Haemoglobin electrophoresis
Types of Anaemia
·
Anaemia from blood loss: Haemorrhage or continued slow bleeding
will cause anaemia.
·
Iron deficiency Anaemia: It may result
·
from faulty eating habits (Poor diets or hurrying meals).
·
Pernicious Anaemia: A patient with pernicious Anaemia lacks
substances in the gastric juice called instrinsic factor,
·
which is necessary to enable the body to absorb vitamin B12 from food.
·
Sickle cell anaemia: It is genetic disease in which the red
blood cells become sickle in shape due to the presence of abnormal haemoglobin.
·
Aplastic anaemia: It results from disease of the bone
marrow (where most blood cells are produced.) whereby the marrow is destroyed.
·
Megaloblastic anaemia: It is caused by deficiency of the vitamin
B12 and folic acid. This
shows identical bone marrow and peripheral blood changes, because both vitamins
are essential for normal DNA synthesis.
·
Haemolytic anaemia: The erythrocyte has a shortened life
span.
Management
·
Anaemia from blood loss: Replace the blood cells by transfusion
and at times administering iron supplements.
·
Iron-Deficiency Anaemia: Take extra iron containing food.
·
Pernicious Anaemia: Take vitamin B12 containing foods and
injection every 2 or 3 weeks will allow the person to live normally.
·
Sickle cell Anaemia: Citadels citrate, pentoxifylline,
vanillin oil as anti sickly effects evaluated as adjunctive therapy for sickle
cell anaemia. Blood transfusion and folic acid therapy is administered.
·
Aplastic anaemia: Two methods of managements are currently
employed. Bone marrow transplantation and Administration of immunosuppressive
therapy with entity.
·
Megaloblastic anaemia: Injection B12 is administered, provide nutritious diet
and folic acid 1 mg per day.
Nursing Management
·
Offer small amount of foods at frequent intervals
·
Provide iron-rich foods and vitamins.
·
Teach and assist with good hygienic practices
·
Good dietary habits
Complication
·
Mental sluggishness
·
Growth retardation
·
Delayed puberty related to growth retardation
·
Cardiac failure related to collapse and shock resulting in death
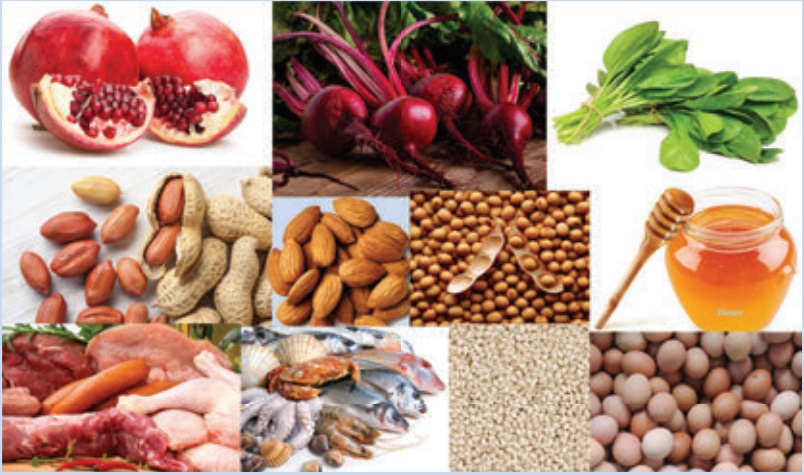
Food rich in Iron: Spinach, Beetroot, Apple, Pomegranate, Soy Beans, Nuts,Honey, Dates, Egg, Sesame Seeds, Seafood and all kind of Meats.

Related Topics