Chapter: Medical Electronics : Assist Devices and Bio-Telemetry
Cardiac Pacemakers
CARDIAC PACEMAKERS
Definition:
A device
capable of generating artificial pacing impulses and delivering them to heart
is known as pacemaker system or pacemaker.
· It consists of a pulse generator and electrodes. Sino Atrial node is
responsible for the starting of heart beat, hence it is called as Natural
Pacemaker.
Types of pacemakers:
Ø Internal
pacemaker
Ø External pacemaker
1. INTERNAL PACEMAKER
·
It is placed inside the body. It may be permanently
implanted on the patients whose SA nodes are failed to function or those who
suffered from permanent heart block.
·
Internal pacemaker systems are implanted with the
pulse generator placed in a
surgically
developed pocket below the right or left clavicle, in left sub costal region.
·
In case of women it is placed beneath the left or
right major pectoral’s muscle.
·
Internal leads are connected to the electrodes that
directly contact the surface of the myocardium.
·
The exact location of the pulse generator used in
the internal pacemaker system depends on the following factors.
Ø Type and
nature of the electrode used.
Ø Nature of
the cardiac problems.
Ø Mode of
operation of the pacemaker system.
·
There is no external connection for applying power.
So the pulse generator should be completely self contained with a battery,
which is capable of operating continuously for a specified period.
2. EXTERNAL PACEMAKER
·
It consists of an externally placed pulse generator
circuit connected to the electrodes placed on the myocardium.
·
Temporary heart irregularities or disorders.
·
Treating the patient from arrhythmias.
·
Treatment of coronary patient and during the
cardiac surgery.
·
It consists of pulse generators. They are placed m
the body and connected normally to the electrode with the help of wires
introduced into the right ventricle.
·
The pulse generator may be strapped to the lower
arm of the patient.
TYPES OF PACING MODES
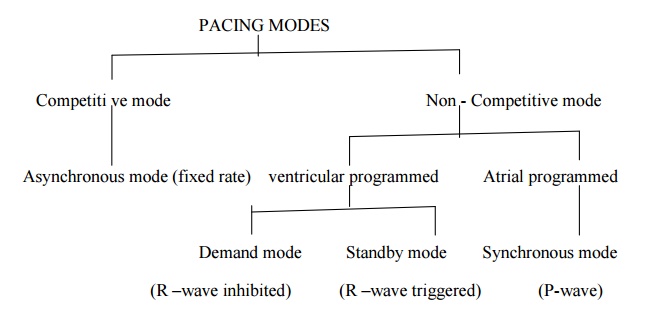
VENTRICULAR ASYNCHRONOUS
PACEMAKER (FIXED RATE PACEMAKER)
·
It can be implemented in atrium or ventricle.
·
Suitable for patients who are suffered by total AV
block, atrial arrhythmia.
·
It consists of square wave generator and monostable
multivibrator circuit. The period square
Wave generator is given as T.
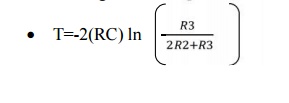
T can be
modified by changing the R,C,R2,R3 values.
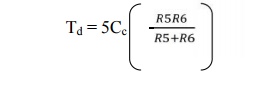
Pulse
duration is given by
Disadvantages:
·
Heart beat rate cannot be changed.
·
If it is fixed in atrium, atrium beat at a fixed
rate. If ventricle beat at a different rate, and then it leads to a severe
problem. Ventricular fibrillation may be occurred.
VENTRICULAR SYNCHRONOUS PACEMAKER (STANDBY
PACEMAKER)
·
Suitable for the patients who are suffered by short
period of AV block.
·
Electrode placed in the right ventricle of heart.
This electrode is used to sense the R-wave.
·
If ventricular contractions are absent, then the
pacemaker provides the impulses. This type of pacemaker does not compete with
the normal heart activity.
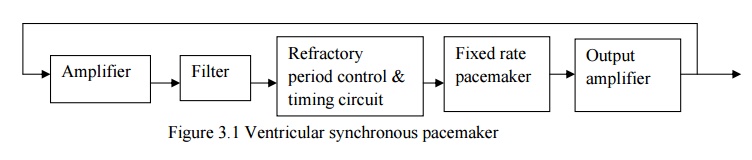
·
Electrode is used to detect the heart rate and it
is given to the amplifier and filter circuit. Because heart rate amplitude is
very low. Amplifier is used to amplify the cardiac signal. Filter is used to
remove unwanted noise signal.
·
Signal is given to refractory period control and
timing circuit.
·
R-wave is below the certain level, at that time
only, this pacemaker will deliver the pulses.
Advantages:
·
Ventricular fibrillation is avoided.
·
When R-wave is normal , then fixed rate pacemaker
block is not in ON condition, so power consumption is reduced.
Disadvantages:
·
Very sensitive to electromagnetic interferences.
·
No synchronization between atrial and ventricular
contraction.
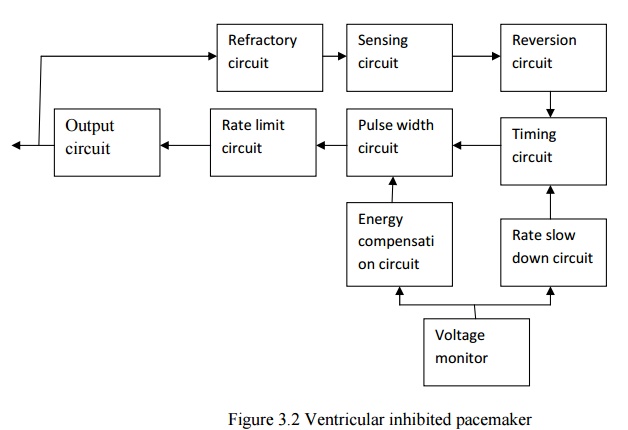
VENTRICULAR INHIBITED PACEMAKER (DEMAND PACEMAKER)
·
Comparator determines the pacing rate of the pulse generator.
·
Output is given to second RC network.The pulse
width circuit determines the duration of the stimulating pulses.
·
Rate limiting circuit disables the comparator for a
short interval and limits the pacing rate.
·
Output circuit provides a voltage pulse to
stimulate the heart.
·
Voltage monitor circuit senses the cell depletion
and controls the rate slow down circuit and energy compensation circuit.
·
Rate slow down circuit shuts off some current to
the basic timing to slow down pulse rate during cell depletion.
·
Energy compensation circuit causes the pulse
duration unit to increase the battery voltage, when it decreases and it is used
to supply the energy to heart.
·
Sensing circuit detects a spontaneous R-wave and
resets the oscillator timing capacitor.
·
Reversion circuit helps the amplifier to detect
spontaneous R wave in the presence of low level continuous wave interference.
·
In the absence of R wave the circuit allows the
oscillator to produce pacing pulses at its present rate.
·
The inhibited pacemaker allows the heart to pace at
its normal rhythm when it is able to do.
·
If the R wave is missing for a preset period of
time, then the pacemaker will turn ON and provide the heart a stimulus. Hence
it is termed as Demand pacemaker.
ATRIAL SYNCHRONOUS PACEMAKER
·
P wave is sensed and picked by the electrode fixed
on the atrium. It is given to the amplifier circuit.
·
Amplifier circuit is used to amplify the
P-waveform.
·
Circuit is used to give the delay 0.12 second.
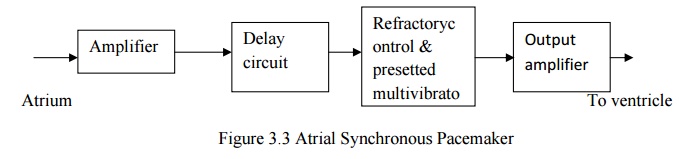
·
The output of the delay circuit given to refractory
control and preset multivibrator block.
·
If the P wave amplitude is not in normal value,
then fixed rate pacemaker will turn ON. When P-wave amplitude is normal, then
fixed rate pacemaker is OFF.
·
If fixed rate pacemaker is ON, then the output is
given to amplifier. The amplified signal is given to ventricle through
electrode.
·
Refractory control circuit provide some time delay,
because pacemaker pulse is too large.
ATRIAL SEQUENTIAL VENTRICULAR INHIBITED PACEMAKER
·
It is used to stimulate both atrial and ventricles.
It is a demand pacemaker, so based on the patients need, it provides the
impulses.
·
In the modern pacemakers, magnet is placed over the
pacemaker on the skin of the patient. This magnet is used to activate the reed
switch. This switch, switches the pacemaker into any one of the mode of
operation, either to give the impulse for atrial or to ventricle.
COMPONENTS OF PACEMAKER
· Pulse generator
·
Electrodes
·
Battery
METHODS OF STIMULATION OF PACEMAKER
·
External stimulation- Used to restart the normal
rhythm of the heart in case of cardiac standstill.
·
Internal stimulation-It prevents normal self
triggering of the heart.
Related Topics