Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 11 : Functions
C++: Accessing a function
Accessing a function
The user-defined function should be called explicitly using its name and the required arguments to be passed. The compiler refers to the function prototype to check whether the function has been called correctly. If the argument type does not match exactly with the data type defined in the prototype, the compiler will perform type conversion, if possible. If type conversion is impossible, the compiler generates an error message.
Example :
1. display() : calling the function without a return value and without any argument
2. display ( x, y) : calling the function without a return value and with arguments
3. x = display() : calling the function with a return value and without any argument
4. x = display (x, y) : calling the function with a return value and with arguments
1. Formal Parameters and Actual Parameters or Arguments
Arguments or parameters are the means to pass values from the calling function to the called function. The variables used in the function definition as parameters are known as formal parameters. The constants, variables or expressions used in the function call are known as actual parameters.
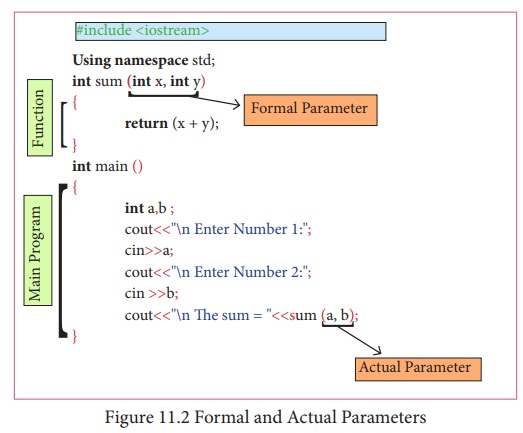
2. Default arguments
In C++, one can assign default values to the formal parameters of a function prototype.
The Default arguments allows to omit some arguments when calling the function.
When calling a function,
• For any missing arguments, complier uses the values in default arguments for the called function.
• The default value is given in the form of variable initialization.
Example : void defaultvalue(int n1=10, n2=100);
• The default arguments facilitate the function call statement with partial or no arguments. Example : defaultvalue(x,y);
defaultvalue(200,150);
defaultvalue(150);
defaultvalue(x,150);
The default values can be included in the function prototype from right to left, i.e., we cannot have a default value for an argument in between the argument list.
Example : void defaultvalue(int n1=10, n2);//invalid prototype
void defaultvalue(int n1, n2 = 10);//valid prototype
3. Constant Arguments
The constant variable can be declared using const keyword. The const keyword makes variable value stable. The constant variable should be initialized while declaring. The const modifier enables to assign an initial value to a variable that cannot be changed later inside the body of the function.
Syntax :
<returntype><functionname> (const <datatype variable=value>)
Example:
• int minimum(const int a=10);
• float area(const float pi=3.14, int r=5);
Program 11.16
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
double area(const double r,const double pi=3.14)
{
return(pi*r*r);
}
int main ()
{
double rad,res;
cout<<"\nEnter Radius :";
cin>>rad;
res=area(rad);
cout << "\nThe Area of Circle ="<<res;
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter Radius :5
The Area of Circle =78.5
If the variable value “r” is changed as r=25; inside the body of the function “area” then compiler will throw an error as “assignment of read-only parameter 'r'"
double area(const double r,const double pi=3.14)
{
r=25;
return(pi*r*r);
}
Related Topics