Chapter: Fundamentals of Database Systems : File Structures, Indexing, and Hashing : Disk Storage, Basic File Structures, and Hashing
Buffering of Blocks
Buffering of Blocks
When several blocks need to be transferred from disk to main memory and
all the block addresses are known, several buffers can be reserved in main
memory to speed up the transfer. While one buffer is being read or written, the
CPU can process data in the other buffer because an independent disk I/O
processor (controller) exists that, once started, can proceed to transfer a
data block between memory and disk independent of and in parallel to CPU
processing.
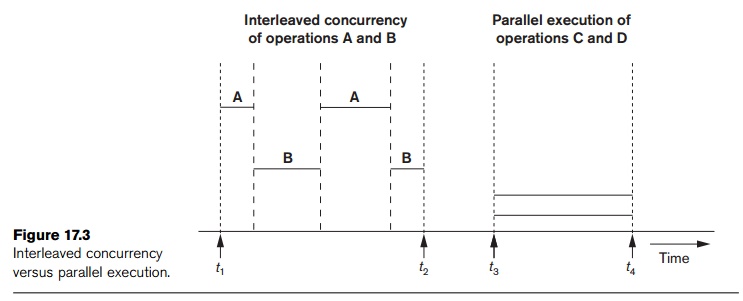
Figure 17.3 illustrates how two processes can proceed in parallel.
Processes A and B are running concurrently
in an interleaved fashion, whereas
processes C and D are running concurrently
in a parallel fashion. When a single
CPU controls multiple processes, parallel execution is not possible. However,
the processes can still run concurrently in an interleaved way. Buffering is
most useful when processes can run concurrently in a parallel fashion, either
because a separate disk I/O processor is available or because multiple CPU
processors exist.
Figure 17.4 illustrates how reading and processing can proceed in
parallel when the time required to process a disk block in memory is less than
the time required to read the next block and fill a buffer. The CPU can start
processing a block once its transfer to main memory is completed; at the same
time, the disk I/O processor can be reading and transferring the next block
into a different buffer. This technique is called double buffering and can also be used to read a continuous stream
of blocks from disk to memory. Double buffering permits continuous reading or
writing of data on consecutive disk blocks, which eliminates the seek time and
rotational delay
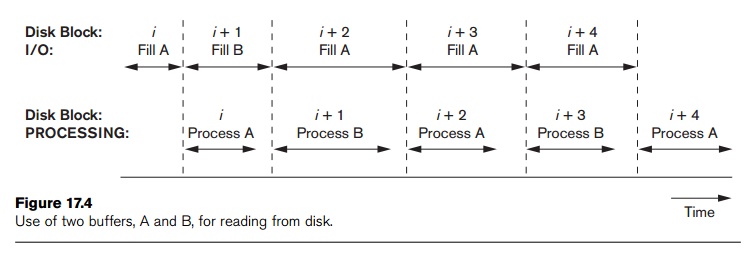
for all but the first block transfer. Moreover, data is kept ready for
processing, thus reducing the waiting time in the programs.
Related Topics