Chapter: Basic Electrical and electronics : Digital Electronics
Boolean Algebra
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA
Boolean
algebra is an algebraic structure defined by a set of elements, B, together
with two binary operators, + and., provider that the following postulates are
satisfied.
T1:
Commutative Law
(a)A+B = B+A
(b)
A B = BA
T2:
Associative Law
(a) (A+B) +C = A+ (B+C)
(b) (A B) C = A (B C)
T3:
Distributive Law
(a) A (B +C) = A B + AC
(b) A + (B C) = (A +B) (A+C)
T4:
Identity Law
(a) A+A =A
(b) A A =A
T5:
Negative Law
(a) (A’) =A’
(b) (A’’) = A
T6:
Redundant Law
(a) A+AB=A
(b) A (A +B) =A
T7: Null
Law
(a)0 + A = A
(b) 1 A = A
(c) 1 + A = 1
(d) 0 A = 0
T8:
Double Negation Law
(a) A’ +A=1
(b) A’ A=0
T9:
Absorption Law
(a) A+A’B =A+B
(b) A (A’ + B) =AB
T10: De
Morgan's Theorem
(a) (A+B)’ = A’ B’
(b) (AB)’ = A’+B’
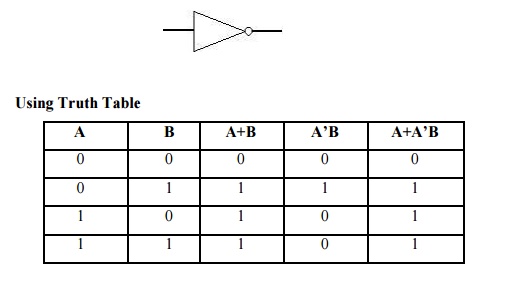
Example 1:
Using
theorems,
A + A’ B = A l + A’ B
= A (l + B) + A’B
=A + AB + A’B
=A + B (A + A’)
= A + B
Using
Truth Table
1
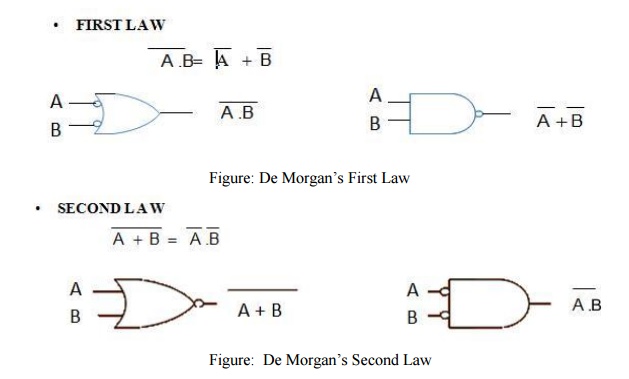
Verification Of De Morgan's Theorems:
•
De
Morgan's First Theorem states:
The complement of a product
of variables is equal to the sum of the complements of the individual variables
•
De
Morgan's Second Theorem states:
The complement of sum of variables is equal to
the product of the complements of the dividable variables
Related Topics