Chapter: Civil : Mechanics Of Solids : Transverse Loading On Beams And Stresses In Beam
Beam shear
Beam shear
Beam shear is defined as the internal shear
stress of a beam caused by the shear force applied to the beam.
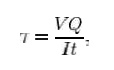
where
V = total shear force at the location in question;
Q = statical moment of area;
t =
thickness in the mat erial perpendicular to the shear;
I =
Moment of Inertia of the entire cross sectional area.
This formula is also known as t he Jourawski
formula.[1]
Semi-monocoque shear
Shear stresses within a semi-
monocoque structure may be calculated by idealizing the cross-section of the
structure into a set of stringers (carrying only axial loads ) and webs
(carrying only shear flows). Dividing th e shear flow by the thickness of a
given portion of the semi-monocoque structure yields the shear stress. Thus,
the maximum shear stre ss will occur either in the web of maximum shear flo w
or minimum thickness.
Also constructions in soil
can fail due to shear; e.g., the we ight of an earth-filled dam or dike may
cause th e subsoil to collapse, like a smalllandslide.
Impact shear
The maximum shear stress crea ted in a solid
round bar subject to impact is g iven as the equation:
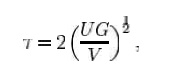
where
U =
change in kinetic e nergy;
G =
shear modulus;
V =
volume of rod;
And
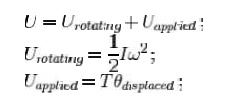
Related Topics