Chapter: Ophthalmology: The Eyelids
Basal Cell Carcinoma
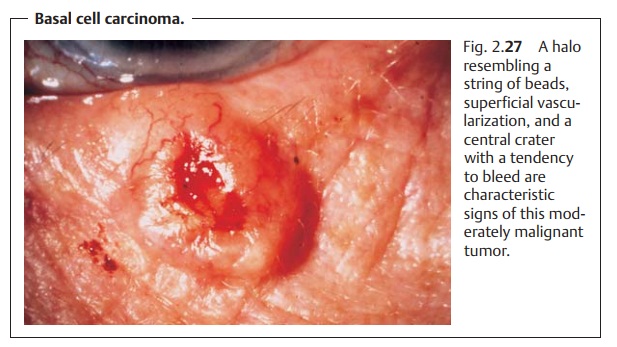
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Definition
Basal cell carcinoma is a frequent, moderately
malignant, fibroepithelial tumor that can cause severe local tissue destruction
but very rarely metastasizes.
Epidemiology:
Approximately 90% of all malignant eyelid
tumors are basalcell carcinomas. Their incidence increases with age. In
approximately 60% of all cases they are localized on the lower eyelid. Morbidity in sunny countries is 110 cases per 100000
persons (in central Europe approximately 20 per 100000 persons). Dark-skinned people are affected significantly less often.
Gender is not a predisposing factor.
Etiology:
Causes of basal cell carcinoma may include a
genetic disposition.Increased exposure to
the sun’s ultraviolet radiation, carcinogenic substances (such as arsenic),
and chronic skin damage can also lead
to an increased inci-dence. Basal cell carcinomas arise from the basal cell
layers of the epidermis and the sebaceous gland hair follicles, where their
growth locally destroys tissue.
Symptoms:
Typical characteristics include a firm,
slightly raised margin (ahalo resembling
a string of beads) with a central
crater and superficial
vascular-ization with an increased tendency to bleed (Fig. 2.27).
Ulceration with “gnawing” peripheral
proliferation is occasionally referred to as an ulcus rodens; an ulcus
terebans refers to deep infiltration with invasion of cartilage and bone.
Diagnostic considerations:
The diagnosis can very often be made on
thebasis of clinical evidence. A biopsy is indicated if there is any doubt.
Loss of the eyelashes in the vicinity of the
tumor always suggests malig-nancy.
Treatment:
The lesion is treated by surgical excision within a margin ofhealthy tissue. This is the safest method. If a radical procedure is not feasible, the only remaining options are radiation therapy or cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen.
Prognosis:
The changes of successful treatment by surgical
excision are verygood. Frequent follow-up examinations are indicated.
The earlier a basal cell carcinoma is
detected, the easier it is to remove.
Related Topics