Chapter: Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications: Drugs Used in Dermatological Disorders
Antimicrobial Agents
ANTIMICROBIAL
AGENTS
Systemic Antibiotics
Antibiotics are used in
dermatology for both infectious and noninfectious skin eruptions. Noninfectious
skin eruptions, such as acne vulgaris and acne rosacea, are often treated with
systemic antibiotics. The mechanism of action is not clear, although
tetracycline inhibits li-pases derived from resident flora in the sebaceous
folli-cle (Staphylococcus epidermidis,
Propionibacterium ac-nes). These lipases cleave irritating fatty acids from triglycerides in sebum, presumably
contributing to cuta-neous inflammation.
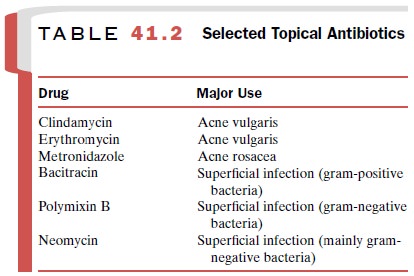
Topical Antibiotics
Topical antibiotics are
helpful in acne vulgaris and acne rosacea and probably in reducing the
frequency of in-fections related to intravenous catheters. One drug, mupirocin
(Bactroban), is effective in treating
impetigo contagiosa. Mupirocin binds to bacterial isoleucyl-transfer RNA
synthetase and prevents the incorpora-tion of isoleucine into protein
sequences. Mupirocin is most effective against gram-positive bacteria. Toxicity
is uncommon.
Another topical antibiotic,
metronidazole, is effec-tive in the treatment of acne rosacea. Metronidazole is
a synthetic nitroimidazole derivative that reduces in-flammation by an unknown
mechanism. Other selected topical antibiotics are listed in Table 41.2.
Related Topics