Chapter: Health Management in Aquaculture: Immunity and biological methods of disease prevention and control
Antibody Production - The fish immune system
Antibody Production
Plasma Cells
Plasma cells are the effector cells of humoral immunity. They synthesize and secrete antibodies (IgM and IgG). Plasma cells are B lymphocytes that have been activated by interaction with their matching antigen. The antigen recep-tors on the membranes of unstimulated B lymphocy’tes are IgM and IgD class antibodies that have the same specificity as the IgG that they will eventually produce as plasma cells. Plasma cells are mostly located in lymphoid organs (but not in the thymus) but are sometimes released into the blood.
The purpose of B lymphocyte stimulation is to form enough plasma cells to produce useable amounts of antibodies. It is a complex process. Besides the B lymphocytes themselves, it involves accessory cells (e.g. macrophages) and a specific class of T lymphocytes (helper cells). It also depends on the presence of special membrane proteins (major histo-compatibility or MHC proteins) on the surface of these cells and the release of different paracrine and autocrine chemical messengers (cytokines) by them.
There are two classes of MHC proteins, MHC-I and MHC-II. All cells (except RBC’s) have MHC-I proteins. Only a few cell types have MHC-II proteins. These include macrophages and other accessory cells (including B lymphocytes) that can function as Antigen Presenting Cells (or APC’s presenting antigens to lym-phocytes).
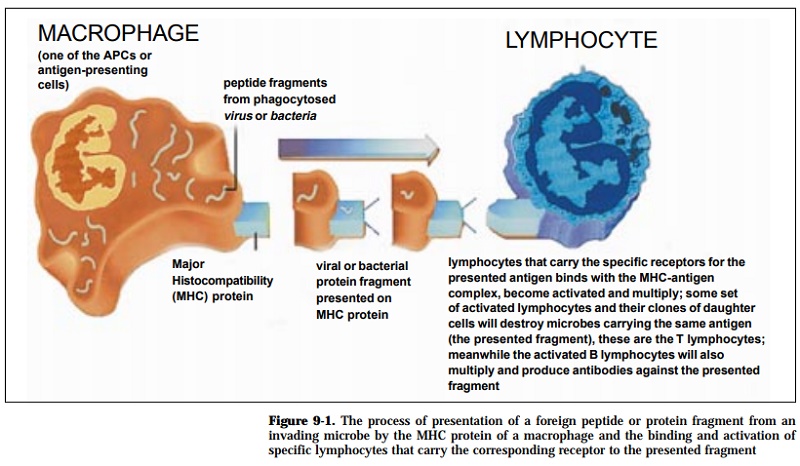
Accessory cells (such as APC’s) ingest antigens and partially digest them. Frag-ments of the antigens (containing the haptens) are combined with MHC-II pro-teins and then together they are inserted into the plasma membrane. Helper T lymphocytes can recognise the MHC-I protein-hapten complexes if they also have receptors that can bind to the hapten. Recognition (or when the receptor on the lymphocyte is a complimentary match to the presented antigen) triggers the release of several kinds of cytokine (interleukins). The interplay between cell-to-cell contact and chemical co-stimulation is what finally activates the B cell (or B lymphocyte).
The process of B cell stimulation results in mitosis of both the helper T cell and the B cell, with the formation of a clonal population of each. This results in a very large number of cells, all producing identical antibodies specifically against the presented antigen (Figure 9 – 1). Some of the B cells are further activated to become plasma cells, which provides a large enough group of cells to produce enough antibody to combat the antigen while some cells become the long-lived memory cells (see text below and captions in Figure 9 – 1).
Related Topics