Immunology - Antibodies | 12th Zoology : Chapter 8 : Immunology
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 8 : Immunology
Antibodies
Antibodies
Antibodies are immunoglobulin (Ig) protein
molecules synthesized on exposure to antigen that can combine specifically with
the antigen. Whenever pathogens enter our body, the B-lymphocytes produce an
army of proteins called antibodies to fight with them. Thus, they are secreted
in response to an antigen (Ag) by the effect of B cells called plasma cells.
The antibodies are classified into five major categories, based on their
physiological and biochemical properties. They are IgG (gamma), IgM
(mu), IgA (alpha), IgD (delta) and IgE (epsilon).
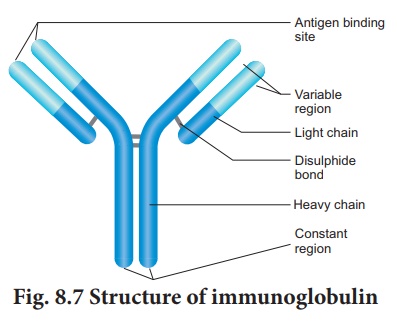
In the 1950s, experiments by Porter and Edelman
revealed the basic structure of the immunoglobulin. An antibody
molecule is Y shaped structure that comprises of four polypeptide
chains, two identical light chains (L) of molecular weight 25,000 Da
(approximately 214 amino acids) and two identical heavy chains (H) of
molecular weight 50,000 Da (approximately 450 amino acids). The polypeptide
chains are linked together by di-sulphide (S-S) bonds. One light chain is
attached to each heavy chain and two heavy chains are attached to each other to
form a Y shaped (Fig. 8.7) structure. Hence, an antibody is represented
by H2 L2. The heavy chains have
a flexible hinge region at their approximate middles.
Each chain (L and H) has two
terminals. They are C - terminal (Carboxyl) and amino or N-terminal. Each chain
(L and H) has two regions. They have variable (V) region
at one end and a much larger constant (C) region at the other end.
Antibodies responding to different antigens have very different regions but
their (C) regions are the same in all antibodies. In each arm of the monomer
antibody, the (V) regions of the heavy and light chains combines to form an
antigen – binding site shaped to ‘fit’ a specific antigenic determinant.
Consequently each antibody monomer has two such antigen – binding regions. The
(C) regions that forms the stem of the antibody monomer determine the antibody
class and serve common functions in all antibodies.
The functions of immunoglobulin are agglutination, precipitation, opsonisation, neutralization etc.,
Related Topics