Chapter: Plant Biochemistry: Phenylpropanoids comprise a multitude of plant secondary metabolites and cell wall components
Anthocyanins are flower pigments and protect plants against excessive light
Anthocyanins are flower pigments and protect plants against excessive light
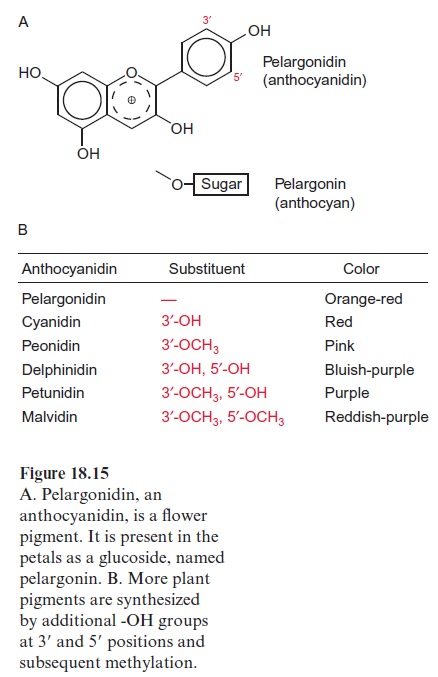
Carotenoids provide yellow and orange flower pigments. Other widely distributed flower pigments are the yellow chalcones, light yellow flavones, and red and blue anthocyanins. Anthocyanins are glucosides of anthocyanidins (Fig. 18.15) in which the sugar component, consisting of one or more hexoses, is usually linked to the -OH group of the pyrylium ring. Anthocyanins are contained in the vacuole. They are transported as glutathione conjugates via the glutath-ione translocator to the vacuole and are deposited there. The anthocyanin pelargonin, shown in Figure 18.15, contains pelargonidin as chromophore. The introduction of two -OH groups at 3’ and 5’ positions of the phenyl residue by P450 dependent monooxygenases and their successive methylation yields five additional flower pigments, each with a different color. Hydroxylations at other positions result in even more pigments. A change in the pH in the vacuole leads additionally to alterations of the color. This in part explains the change of color when plants fade. Moreover, the color of the pigment is altered by the forma-tion of complexes with metal ions. Thus, upon complexation with Al+++ or Fe+++, the color of pelargonin changes from orange red to blue. These various pigments and their mixtures lead to the multitude of color nuances of flowers. With the exception of pelargonidin, all the pigments listed in Figure 18.15 are found in the flowers of petunia. To date, 35 genes that are involved in the coloring of flowers have been isolated from petunia.
Anthocyanins not only contain flower pigments to attract pollen-trans-ferring insects, but also function as protective pigments for shading leaf mesophyll cells. Plants in which growth is limited by environmental stress factors, for instance phosphate deficiency, chilling, or high salt content of the soil, often have red leaves, due mainly to the accumulation of anthocy-anins. Stress conditions, in general, reduce the utilization of NADPH and ATP, which are provided by the light reactions of photosynthesis. Shading the mesophyll cells by anthocyanins decreases the light reactions and thus prevents overenergization and overreduction of the photosynthetic electron transport chain.
Related Topics