Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Genitourinary system
Anion gap - Investigations and procedures
Anion gap
Anion gap calculation is useful in metabolic acidosis, to differentiate
causes. It is a measure of the unestimated anions (phosphate, ketones, lactate)
and cations. The formula used to calculate the anion gap varies from source to
source, and the normal range depends on the methods by which the laboratory
measures each electrolyte. For example:
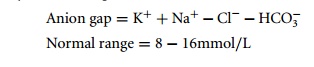
In metabolic acidosis, an increased anion gap occurs due to raised acid
levels:
·
Lactic acidosis (exercise, shock,
hypoxia, liver failure).
·
Acid ingestion (aspirin, ethylene
glycol).
·
Ketoacidosis.
·
Uraemia.
In metabolic acidosis, a normal anion gap indicates that there is
failure to excrete acid or loss of base:
·
Failure to excrete acid occurs in
renal tubular disease and Addison’s disease.
·
Loss of base (bicarbonate) occurs
in diarrhoea, proximal renal tubular acidosis, or iatrogenically, due to
carbonic anhydrase inhibitor or ureterosigmoidostomy.
Related Topics