Chapter: Obstetrics and Gynecology: Embryology and Anatomy
Anatomy of Vulva and Perineum
Vulva and Perineum
The perineum comprises the area of the
surface of the trunk between the thighs and the buttocks, extending from the
coccyx to the pubis. Anatomists also use the term
“perineum” torefer to the shallow compartment
that lies deep to this area and inferior to the pelvic diaphragm.
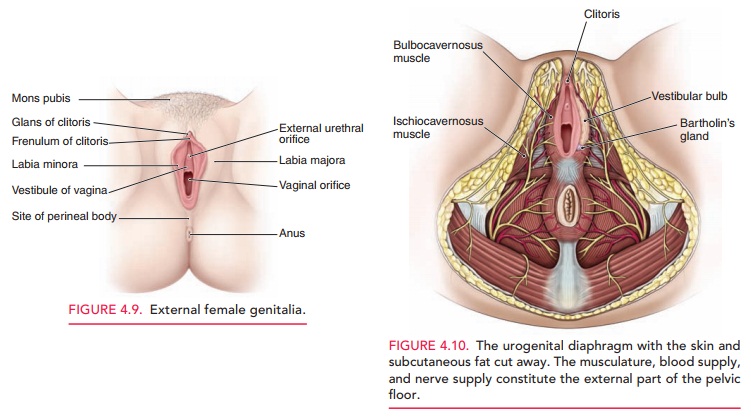
The vulva contains the labia majora, labia minora, mons pubis,
clitoris, vestibule, and ducts of glands that open into the vestibule (Fig.
4.9). The labia majora are folds of
skin with underlying adipose tissue, fused anteriorly with the mons pubis and
posteriorly at the perineum. The skin of the labia majora contains hair
follicles as well as seba-ceous and sweat glands. The labia minora are narrow skin folds lying inside the labia majora.
The labia minora merge anteriorly with the prepuce and frenulum of the
clitoris, and posteriorly with the labia majora and the perineum. The labia
minora contain sebaceous and sweat glands, but no hair follicles, and there is
no underlying adipose tissue. The clitoris,
which is located anterior to the labia minora, is theembryologic homolog of
the penis. It consists of two crura (corresponding to the corpora cavernosa in
the male) and the glans, which is found superior to the point of fusion of the
crura. On the ventral surface of the glans is the frenu-lum, the fused junction of the labia minora.
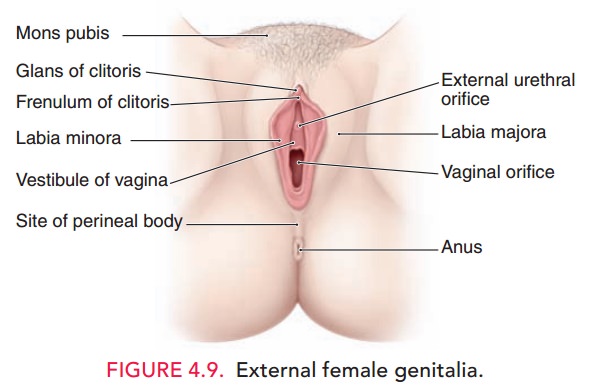
The vestibule lies between the labia minora and
is bounded anteriorly by the clitoris and posteriorly by the perineum. The
urethra and the vagina open into the vestibule in the midline. The ducts of Skene (paraurethral) glands
and Bartholinglands also empty into
the vestibule. Secretions from theBartholin glands are responsible for sexually
stimulated vaginal lubrication.
The muscles of the vulva
(superficial transverse per-ineal, bulbocavernosus, and ischiocavernosus) lie
superficial to the fascia of the urogenital
diaphragm (Fig. 4.10). The vulva rests on the triangular-shaped urogenital
diaphragm, which lies in the anterior part of the pelvis between the
ischiopubic rami
Related Topics