Chapter: Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications: General Organization and Functions of the Nervous System
Anatomic Differences Between the Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems
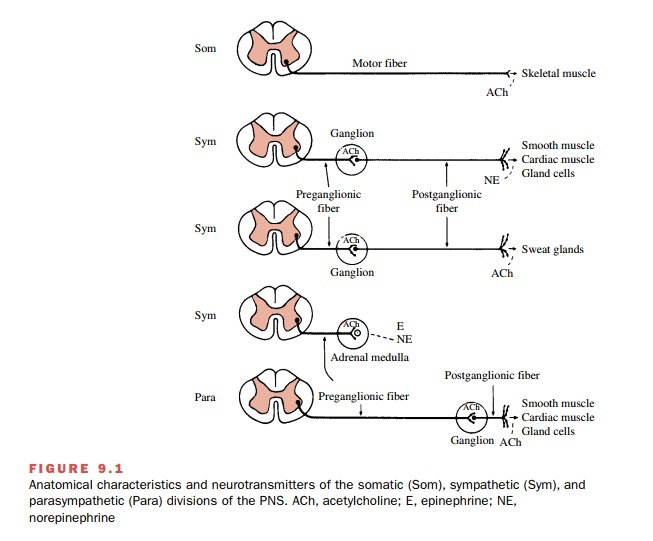
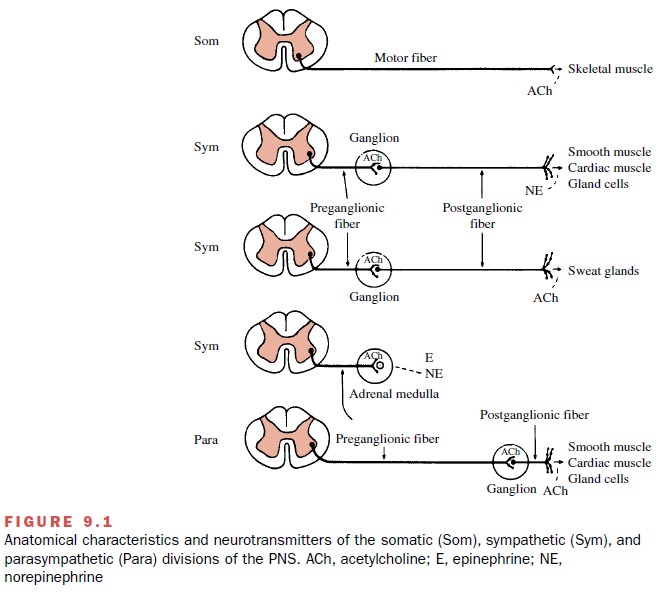
ANATOMIC
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEMS
Anatomical differences
between the peripheral somatic and autonomic nervous systems have led to their
classi-fication as separate divisions of the nervous system. These differences
are shown in Figure 9.1. The axon of a somatic motor neuron leaves the CNS and
travels without interruption to the innervated effector cell. In contrast, two
neurons are required to connect the CNS and a visceral effector cell of the
autonomic nervous system. The first neuron in this sequence is called the preganglionic neuron. The second neuron,
whose cell body is within the
ganglion, travels to the visceral effec-tor cell; it is called the postganglionic neuron.
Related Topics