Chapter: Diseases of The Brain and Nervous System(A Health Education Guide): An overview of the Nervous System
An overview of the Nervous System
AN OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
The Nervous system comprises of the brain, the spinal cord, the nerves emanating from them and their innervations of muscle fibres. The human race is superior and special to the other living beings due to the unique anatomy and physiology of human nervous system. Especially the cortex of the brain (the grey layer of the brain surface) is highly evolved and complex. Other organs of the human beings are similar or even weaker as compared to those of the other animals, but the humanrace proves superior because of the exceptional mental power & ability, as well as logic, memory and vocabulary all due to the cortex of the brain. The cortex consists of approximately 100 billion neurons. According to an estimate, an average person uses about 5 to 10 percent of his brain capacity, but a genius uses his brain up to 15 percent. Therefore it can be said that any person can become a genius by learning how to use his brain more and putting it frequently to task.
An adult human brain is approximately 1200 to 1400 grams in weight. Though our brain weighs only 1 to 2 percent of total body weight, it uses up approximately 25 percent of the oxygen intake of the body and 70 percent of the total glucose available to the body. The lower group of chordate animals do not have a developed organ like brain and therefore their functions are autonomous. So they don’t feel pain, e.g. a fly etc. A large head, in effect does not mean more intellectual capacities. The structure of the brain.matters more than its size.
The outer layer of the brain surface is grey in color and is called cortex, whereas the inner layer is white and is known as white matter.
The brain rests securely inside the skull and is covered by three membranes to protect against friction. These membranes are called the meaninges. They are dura matter (outer most), arachnoid matter (middle) and pia matter (innermost). The inflammation of these membranes is called meningitis e.g. tubercular meningitis. The chambers insidethe brain are known as ventricles. There are four ventricles viz. two lateral ventricles, a third ventricle and a fourth ventricle.
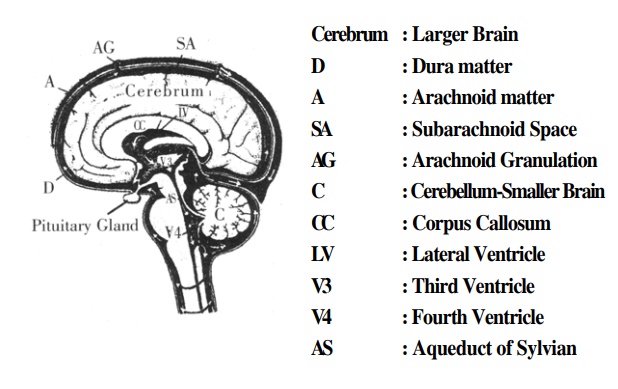
The watery fluid inside these chambers is called C:S.F. It extends right from the centre of the brain to the spinal cord, as well as in the outer membranes of the brain and spinal cord. Any infection or hemorrhage in the brain can be diagnosed easily by the examination of the C.S.F extracted from the spinal cord by a procedure called Lumbar puncture. The functions of C.S.F range from assisting the metabolism of the brain to the prevention of friction: As the cells of the brain perform complex functions, they need extra nourishment and oxygen. This calls for a faster and greater blood supply. If the supply of blood and oxygen to the cortex stops completely for more than five minutes, the cortex stops functioning permanently, resulting in death.
The brain can be divided into three parts viz.
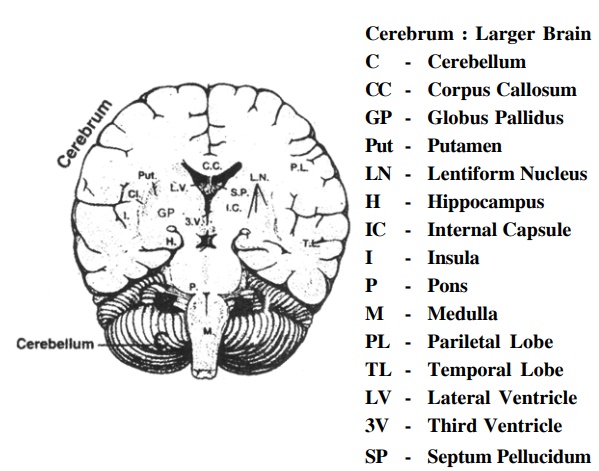
1. Cerebrum, which occupies the larger portion ofthe skull. It is divided into two - left and right - hemispheres. The part joining the two hemispheres is known as corpus callosum.
2. Cerebellum is located in the posterior region ofthe skull and is divided into two - left and right - parts. Its primary function is to maintain the equilibrium of the body.
3. The brain stem, which joins the two sides of the brain, consists of mid-brain, pons and medullaoblongata, which truncate into the spinal cord.
The cerebrum can be subdivided into four parts as per their functions:
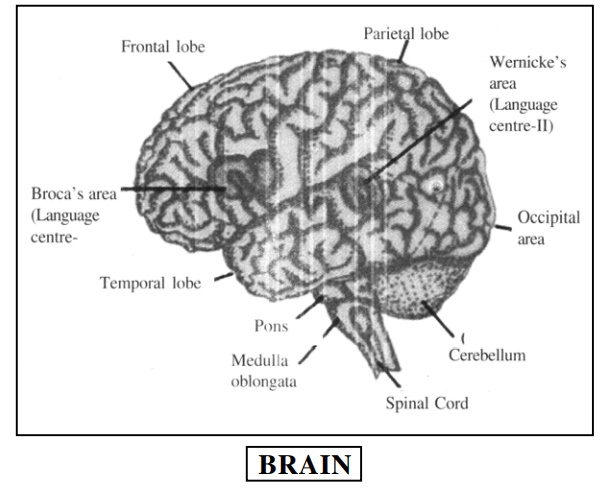
1. Frontal (The anterior part)
2. Parietal (The lateral upper portion)
3. Temporal (The lateral lower portion)
4. Occipital lobes (The posterior part)
The right side of the brain is responsible for the motor and sensory functioning of the left side of the body and the opposite is true for the left-brain. The left-brain is also responsible for the linguistic expressive ability. The frontal lobe is basically responsible for the movements of the limbs, the personality and the behavior of an individual. The parietal lobe analyzes emotions and is also associated with mathematical powers. The temporal lobe and the limbic system are associated with memory as well as basic instincts, and according to some it can be the seat of special powers like the sixth sense, etc. The centre for hearing is also located here. Occipital lobe is analytic centre in the brain for vision. The left side of the brain of a right handed person (who uses his right hand for writing, eating, throwing etc.) is dominant and contains the centre for language, mathematical and logicalabilities and therefore, can be considered the technical brain of the person. The right brain is associated with sensitivity, creativity and imagination etc. It is worth understanding that brilliant people use the right side of the brain more efficiently.
The location of psyche (mana) in the brain is a controversial issue. According to an opinion mana is present in each cell. However, others believe that the mana may exist either in the temporal lobe, in the limbic circuit, or in the pineal gland of the brain. In fact, there is no anatomical location for the mana. It is actually a complex biochemical and electromagnetic process and it is the limitation of our science and brain that we do not have the proper understanding of this subject. The same thing can also be said for the soul.
The brain also has important cellular clusters namely thalamus and basal ganglia, chemical imbalance in thesecentres causes diseases like Parkinson’s disease, Chorea, Dystonia etc.
Similarly, Hypothalamus is an important centre and is the final control point of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system. It is associated withfunctions of our involuntary muscles, as well as physical processes like stress. This type of nervous system autonomously controls the extremely important functions of the heart, intestines, eyeballs, blood pressure, respiration etc. Pituitary gland, the master controller of all the endocrine glands, is also located in the brain. It regulates the entire hormonal system of the body in an amazing manner. Apart from this, there is an incredible network of various important neurotransmitters like Dopamine, Noradrenalin, GABA, Serotonin, Acetylcholine, Endorphin and Encephalin in the brain and the entire nervous system for the transmission of impulses to and fro. These important neurotransmitters communicate through a series of receptors.
We have thus studied the anatomy of the brain, but brain has some amazingly unique features also, which make man superior to all living beings. There is a kind of electrical impulse emanating from the cells of the brain, which is rhythmic and constant. This is an electrical process.
This electrical impulse travels chemically across one nerve cell to the other through neurotransmitters and receptors which form an amazing network and can transmit information from one part to another in a 1000th fraction of a second.
This is a chemical process.
The brain cells handle metabolism like other cells. Thisis a biological process. Transmission of messages from oneperson’s minds to the other, as in telepathy can be calledan electronic process. Moreover, the human brain is endowedwith developed features like thinking, intelligence, the power to differentiate between good and bad, memory, creativity, etc. At the same time the brain has emotions like care, anger, likes-dislikes and love. Importantly the braingoverns all the basic instincts like hunger, sleep, fear,reproduction etc. Senses like vision, taste, smell, touch and hearing are under the command of brain. Further we are able to communicate our thoughts very easily through language.
Is the entity called psyche (mana) not a part of the brain itself ? Though anatomically the heart is situated in the chest, the way poets have described the emotional heart it appears that in fact they are referring to the mind.
Can we ever expect any of the man-made super computers to have all these features? The amazing thing is that we ourselves can think about our own brain, analyze it; but the one, who has created us, has discreetly left us in the dark about him. Again a human limitation.
The electric impulses of the brain can be detected with the help of an Electroencephalogram (E,E.G). The electrical impulse generated by the posterior part of the brain during waking with eyes closed is known as alpha wave. The frequencies measure 8 to 13 Hz. Normally the frontal cortex generates the beta rhythm measuring 14 to 40 Hz. At times theta activity can be detected in the temporal regionsmeasuring 4 to 7 Hz. and in children it is far more developed. Delta activity in an adult is always abnormal but sometimescan be noted in children while they are asleep. Otherwise the delta activity usually indicates disease of the brain.
In the past few decades, mental maladies have come to be recognized as problems of the brain, and antidotes have emerged as the treatment of choice. Regardless of how one feels about the biological basis of psychiatry today, two facts must be acknowledged. The essence of who we are is encoded in our brain, and brain changes account for the alterations of thought, mood, and behavior that occur in mental illness. The key issue is not whether mental illness is really neural in nature. It is instead the nature of the neural changes that underlie mental problems, and the manner in which treatment should proceed. These sections provide a broad framework of the basic concepts and terms necessary to understand the fundamental processes underlying brain function. For those who love details, following paragraphs may be interesting.
Basic unit - a neuron & neural organisation
As mentioned earlier, the Nervous System comprises of the brain, the spinal cord, the nerves emanating from them and their innervations of muscle fibres (i.e. peripheral nervous system). The brain immediately confronts us with its great complexity. The human brain weighs only 1200 to 1400 gms. but contains about 100 billion neurons. Although that extraordinary number is of the same order of magnitude as the number of stars in the Milky Way, it alone cannot account for the complexity of the brain. A major part of the complexity arises from the rich diversity of nerve cells, or neurons, which the famous neuroanatomist Ramon y Cajal described as “the mysterious butterflies of the soul”.
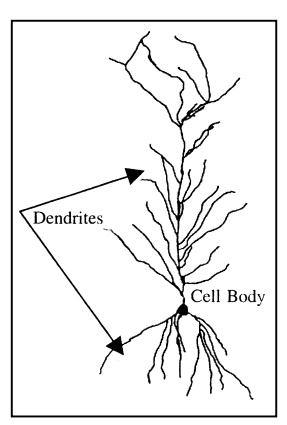
Neurons, or nerve cells, are the basic building blocks of the brain. A neuron has three main parts - a cell body containing the nucleus, dendrites which are specialized branches for receiving information from other neurons, and axons which are specialized branches for sending out information to other neurons. A neuron that has been excited conveys information to other neurons by generating electrical impulse known as action potentials. These signals propagate like waves down the length of the cell’s single axon and are converted to chemical signals at synapses, the contact point between neurons. When the impulse reaches the axon terminals of the presynaptic neuron, it induces the release of neurotransmitter molecules.
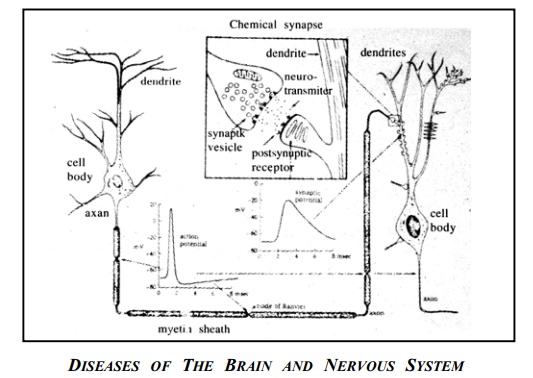
Transmitters diffuse across a narrow cleft and bind to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane. Such binding leads to the opening of ion channels and often, in turn, to the generation of action potentials in the postsynaptic neuron. This, in short, is how neurons communicate.
Many different kinds of neurotransmitters have been identified in the brain, and this variety has enormous implications for brain function. This level of analysis at the synaptic level is particularly relevant for psychiatric and neurological disorders that shed light on the workings of the mind. Further insight into the chemical basis of thinking and behavior depends on obtaining more precise data at multiple levels of neural organization - from the mind all the way down to molecules.
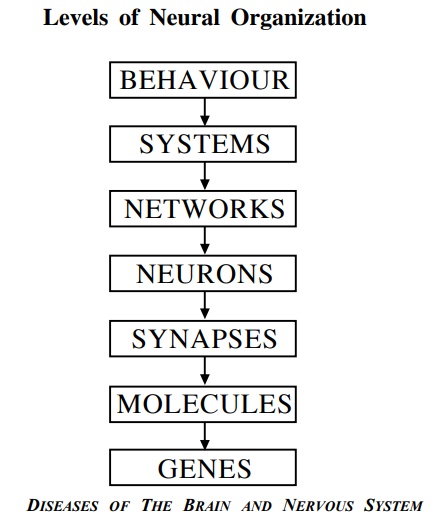
Neuroscience has rapidly emerged as a frontier area of cutting - edge research due to major discoveries at all of these levels of investigation - starting from psychiatry at one end to molecular neurobiology and neurogenetics at the other. The power of the molecule-to-mind approach is evident in many recent advances in the pharmacologic treatment of many debilitating mental disorders such as schizophrenia, anxiety, amnesia, etc.
COMMON DISEASES :
After understanding the basics of the brain, we will now classify the common diseases of the brain and nervous system:
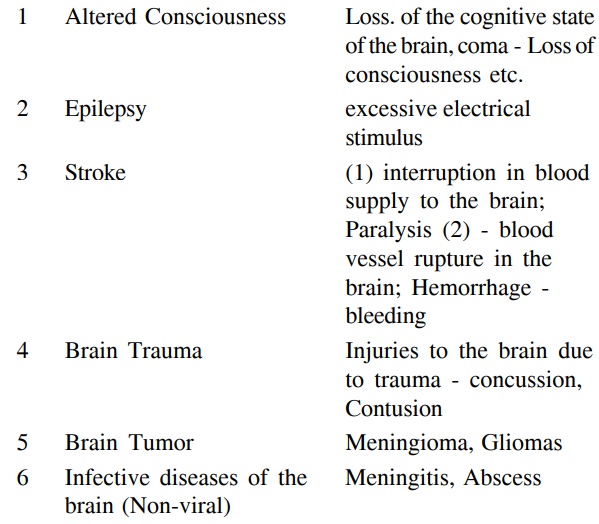

The above mentioned diseases are known as neurological disorders. A neurologist or any experienced physician can treat them. Diseases of the psyche (mana) are called psychiatric disorders e.g. depression, anxiety, psychosis, neurosis, personality problem, psychosexual diseases etc. A qualified psychiatrist should treat these diseases. Normally in psychiatric diseases investigations like CT scan, E.E.G. and Lumber Puncture are normal. Many a times there can be similar symptoms creating confusion. For instance a change in the personality of a patient may either be due to depression or brain tumor (frontal or corpus callosal region). This can result in serious lapse in diagnosis. Therefore, in each psychiatric case a detailed history as wellas physical examination is essential. If in doubt, it is always better to get a test or two (like CT Scan or E.E.G) done, rather than label the patient a psychiatric case in haste. Fortunately, such errors are extremely rare.
At times head injuries in cases of road accidents, falling from a height, or injury due to an instrument, demand immediate emergency treatment. In such cases it is essential that the patient is immediately shifted to a hospital without wasting any time, and given emergency treatment by a neurosurgeon.
After this basic information about the brain, we will now try to understand the various diseases of the brain in detail, in the subsequent chapters. I would like to clarity that above mentioned psychiatric disorders being out of context, they are not discussed here.
Finally, a most important point - It has been observedfrom experience that, though timely, correct diagnosis and proper medications are important for curing a patient, there are other equally important factors to bring a patient to a state of total healing & health which are unfortunately not being given proper importance in modern medicine.
It is important for the patient to have faith in his doctor and have will power, a desire to live, a positive attitude and a disciplined and simple lifestyle, for a quick and complete recovery. This apart, the sympathy of the doctor towards his patient, his honest dedication towards his profession as well as his skill and high character are vital. Also the care and kindness of nursing staff in the ward are equally important.
The care and warmth of family members, friends and relatives, prayers, the social atmosphere of the home and accurate information regarding the disease also playimportant role in the restoration of the health of the patient. All these points are worth taking into consideration and due emphasis should be given to each of them, in the management of a patient. In short, the aim should behealing of a patient and not merely eradication of the disease - symptoms.
Related Topics