Chapter: Health Management in Aquaculture: Fungal diseases
Aflatoxicosis (Red Disease) - Fungal Diseases of Crustaceans
Aflatoxicosis (Red Disease)
CAUSATIVE AGENT:
Aflatoxin produced by Aspergillus flavus and other Aspergillus spp. (Fig. 4-9) which are common contaminants of not-properly stored or expired feeds.
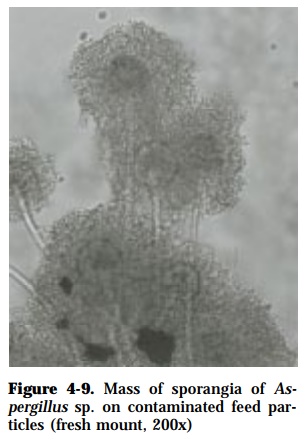
SPECIES AFFECTED:
Penaeus monodon, other Penaeus spp.
GROSS SIGNS:
Yellowish, and eventually reddish discoloration of the shrimp body and ap-pendages can be observed among pond-cultured shrimp juveniles. Affected animals become lethargic with weak swimming activity near pond dikes. Soft shelling can also be observed.
DIAGNOSIS:
Affected shrimps will not survive for more than 30 seconds when collected from the feeding trays. There will also be loss of appetite. Confirmation is by chemical analysis for the presence of aflatoxin in the suspected feed/ingredient.
EFFECTS ON HOSTS:
Histopathologically, necrosis in the tubule epithelium that proceeds from proxi-mal portion of the tubules to peripheral tubule tips in the hepatopancreas can be observed. Growth will be retarded.
PREVENTION AND CONTROL:
Do not use moldy feeds. Feeds should be properly stored (for not more than 6 months) in dry and well-ventilated areas to prevent, or at least minimize growth of fungal contaminants.
Related Topics